User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Cloud Storage
- Web Desktop at a Glance
- Web Configurator
- Storage Manager
- Status Center
- Control Panel
- Videos, Photos, Music, & File Browser
- Administrator
- Managing Packages
- Tutorials
- 14.1 Overview
- 14.2 Windows 7 Network
- 14.3 Windows 7 Network Map
- 14.4 Playing Media Files in Windows 7
- 14.5 Windows 7 Devices and Printers
- 14.6 File Sharing Tutorials
- 14.7 Download Service Tutorial
- 14.8 Printer Server Tutorial
- 14.9 Copy and Flickr Auto Upload Tutorial
- 14.10 FTP Uploadr Tutorial
- 14.11 Web Configurator’s Security Sessions
- 14.12 Using FTPES to Connect to the NAS
- 14.13 Using a Mac to Access the NAS
- 14.14 How to Use the BackupPlanner
- Technical Reference
- Status Screen
- System Setting
- Applications
- Packages
- Auto Upload
- Dropbox
- Using Time Machine with the NAS
- Users
- Groups
- Shares
- WebDAV
- Maintenance Screens
- Protect
- Troubleshooting
- 28.1 Troubleshooting Overview
- 28.2 Power, Hardware, Connections, and LEDs
- 28.3 NAS Starter Utility
- 28.4 NAS Login and Access
- 28.5 I Cannot Access The NAS
- 28.6 Users Cannot Access the NAS
- 28.7 External USB Drives
- 28.8 Storage
- 28.9 Firmware
- 28.10 File Transfer
- 28.11 Networking
- 28.12 Some Features’ Screens Do Not Display
- 28.13 Media Server Functions
- 28.14 Download Service Functions
- 28.15 Web Publishing
- 28.16 Auto Upload
- 28.17 Package Management
- 28.18 Backups
- 28.19 Google Drive
- Product Specifications
- Customer Support
- Legal Information
- Index
Chapter 8 Storage Manager
Cloud Storage User’s Guide
100
1 array wit h m irrored dat a. Data is duplicated across t wo disks, so if one disk fails, t here is still a
copy of t he dat a.
As RAI D 1 uses m irroring and duplexing, a RAI D 1 array needs an even num ber of disks ( t wo or
four for the NAS) .
RAI D 1 capacit y is lim it ed t o the size of t he sm allest disk in the RAI D array. For exam ple, if you
have t wo disks of sizes 150 GB and 200 GB respect ively in one RAI D 1 array, then t he m axim um
capacity is 150 GB and t he rem aining space ( 50 GB) is unused.
Typical applicat ions for RAI D 1 are those requiring high fault t olerance wit hout need of large
am ounts of st orage capacity or top perform ance, for exam ple, accounting and financial dat a, sm all
dat abase syst em s, and ent erprise servers.
RAID 6
RAI D 6 can tolerat e two sim ultaneous drive failures by calculating dual distribut ed parit y data on
st riped dat a across disks. Dual parit y provides ext ra data protection, however, it is slower t o write
than m ost other RAI D levels.
RAI D 6 uses parit y to store redundant dat a on space equal t o the size of t wo disks for lat er dat a
recovery. Therefore, on a RAI D 6 array, only 50% of the space is available as usable capacity. I f you
have four disks of sizes 1TB, 1TB, 2TB, 2TB respectively in one RAI D 6 array, t hen t he m axim um
capacity of t he array is t he capacity of the sm allest drive ( 1TB, 1TB, 2TB, 2TB) * ( Num ber of disks
- 2) = 1TB * ( 4-2) = 2TB. The rem aining space ( 2 TB) is unused.
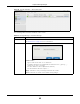
Table 33 RAI D 1
A1 A1
A2 A2
A3 A3
A4 A4
DISK 1 DISK 2
Table 34 RAI D 6
RAID 6
A1 A2 AP AQ
B1 BP BQ B2
CP CQ C1 C2
DQ D1 D2 DP
DISK 1 DISK 2 DISK 3 DISK 4