P-2302R Series VoIP Station Gateway User's Guide
Table Of Contents
- P-2302R Series
- User’s Guide
- Copyright
- Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Interference Statement
- Safety Warnings
- ZyXEL Limited Warranty
- Customer Support
- Table of Contents
- List of Figures
- List of Tables
- Preface
- Introducing the Prestige
- Introducing the Web Configurator
- Wizard Setup
- System Screens
- LAN Setup
- WAN Screens
- Introduction to VoIP
- VoIP Screens
- Phone
- Phone Book
- Phone Usage
- Network Address Translation (NAT) Screens
- Static Route
- Firewall
- Content Filtering
- Remote Management Screens
- Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
- Logs
- Bandwidth Management
- 19.1 Bandwidth Management Overview
- 19.2 Bandwidth Classes and Filters
- 19.3 Proportional Bandwidth Allocation
- 19.4 Application-based Bandwidth Management
- 19.5 Subnet-based Bandwidth Management
- 19.6 Application and Subnet-based Bandwidth Management
- 19.7 Scheduler
- 19.8 Maximize Bandwidth Usage
- 19.9 Bandwidth Borrowing
- 19.10 Configuring Summary
- 19.11 Configuring Class Setup
- 19.12 Configuring Monitor
- Maintenance
- Introducing the SMT
- General Setup
- WAN Setup
- LAN Setup
- Internet Access
- Remote Node Configuration
- Static Route Setup
- Network Address Translation (NAT)
- Enabling the Firewall
- Filter Configuration
- SNMP Configuration
- System Information and Diagnosis
- Firmware and Configuration File Maintenance
- 33.1 Filename Conventions
- 33.2 Backup Configuration
- 33.2.1 Backup Configuration
- 33.2.2 Using the FTP Command from the Command Line
- 33.2.3 Example of FTP Commands from the Command Line
- 33.2.4 GUI-based FTP Clients
- 33.2.5 TFTP and FTP over WAN Management Limitations
- 33.2.6 Backup Configuration Using TFTP
- 33.2.7 TFTP Command Example
- 33.2.8 GUI-based TFTP Clients
- 33.3 Restore Configuration
- 33.4 Uploading Firmware and Configuration Files
- System Maintenance
- Remote Management
- Call Scheduling
- Troubleshooting
- 37.1 Problems Starting Up the Prestige
- 37.2 Problems with the LAN Interface
- 37.3 Problems with the WAN Interface
- 37.4 Problems with Internet Access
- 37.5 Problems with the Password
- 37.6 Problems with the Web Configurator
- 37.7 Problems with a Telephone or the Telephone Port
- 37.8 Problems with Voice Service
- 37.9 Pop-up Windows, JavaScripts and Java Permissions
- Product Specifications
- Wall-mounting Instructions
- Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
- IP Subnetting
- PPPoE
- Triangle Route
- SIP Passthrough
- Index
P-2302R Series User’s Guide
95 Chapter 7 Introduction to VoIP
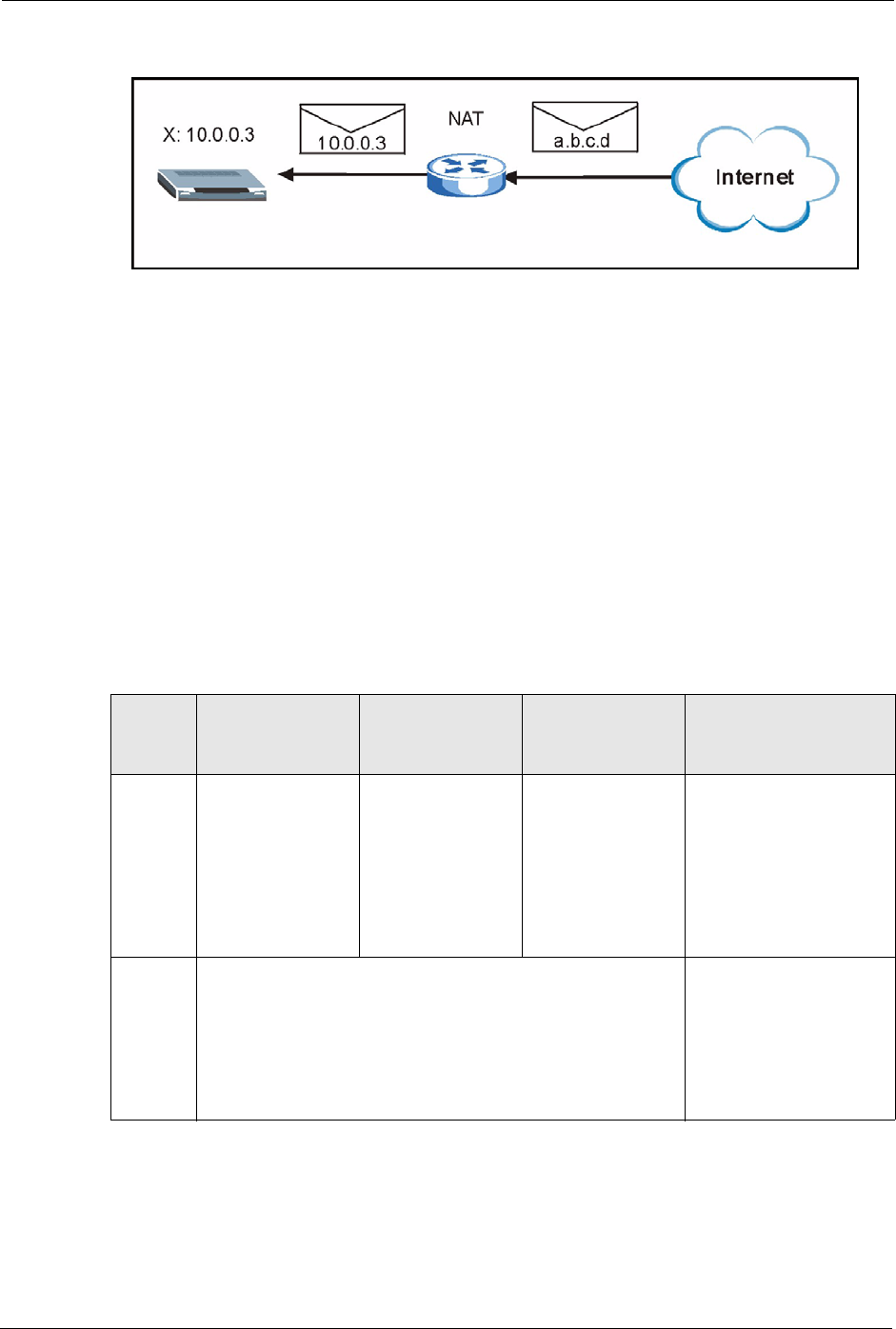
Figure 31 NAT: Incoming
7.3.2 NAT Types
This section discusses the following NAT types that may be implemented on a router in front
of the Prestige.
• Full Cone
• Restricted Cone
• Port Restricted Cone
• Symmetric
The following table summarizes how these NAT types handle outgoing and incoming packets.
Read the following sections for more details and examples.
The examples in these NAT type sections describe NAT translation between internal (private)
and external (public) IP addresses.
Table 20 NAT Types
FULL CONE
RESTRICTED
CONE
PORT
RESTRICTED
CONE
SYMMETRIC
Incoming
Packets
Any external host
can send packets to
the mapped
external IP address
and port.
Only external hosts
with an IP address
to which the internal
host has already
sent a packet can
send packets to the
mapped external IP
address and port.
Only external hosts
with an IP address
and port to which
the internal host
has already sent a
packet can send
packets to the
mapped external IP
address and port.
A host on the external
network can only send
packets to the specific
mapped external IP
address and port that the
NAT router used in
sending a packet to the
external host’s IP address
and port.
Outgoing
Packets
The NAT router maps the internal IP address and port of all
outgoing packets to a single IP address and port on the
external network.
The NAT router maps the
internal IP address and
port of each outgoing
packet to a different
external IP address and
port for each different
destination IP address
and port.










