P-2302R Series VoIP Station Gateway User's Guide
Table Of Contents
- P-2302R Series
- User’s Guide
- Copyright
- Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Interference Statement
- Safety Warnings
- ZyXEL Limited Warranty
- Customer Support
- Table of Contents
- List of Figures
- List of Tables
- Preface
- Introducing the Prestige
- Introducing the Web Configurator
- Wizard Setup
- System Screens
- LAN Setup
- WAN Screens
- Introduction to VoIP
- VoIP Screens
- Phone
- Phone Book
- Phone Usage
- Network Address Translation (NAT) Screens
- Static Route
- Firewall
- Content Filtering
- Remote Management Screens
- Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
- Logs
- Bandwidth Management
- 19.1 Bandwidth Management Overview
- 19.2 Bandwidth Classes and Filters
- 19.3 Proportional Bandwidth Allocation
- 19.4 Application-based Bandwidth Management
- 19.5 Subnet-based Bandwidth Management
- 19.6 Application and Subnet-based Bandwidth Management
- 19.7 Scheduler
- 19.8 Maximize Bandwidth Usage
- 19.9 Bandwidth Borrowing
- 19.10 Configuring Summary
- 19.11 Configuring Class Setup
- 19.12 Configuring Monitor
- Maintenance
- Introducing the SMT
- General Setup
- WAN Setup
- LAN Setup
- Internet Access
- Remote Node Configuration
- Static Route Setup
- Network Address Translation (NAT)
- Enabling the Firewall
- Filter Configuration
- SNMP Configuration
- System Information and Diagnosis
- Firmware and Configuration File Maintenance
- 33.1 Filename Conventions
- 33.2 Backup Configuration
- 33.2.1 Backup Configuration
- 33.2.2 Using the FTP Command from the Command Line
- 33.2.3 Example of FTP Commands from the Command Line
- 33.2.4 GUI-based FTP Clients
- 33.2.5 TFTP and FTP over WAN Management Limitations
- 33.2.6 Backup Configuration Using TFTP
- 33.2.7 TFTP Command Example
- 33.2.8 GUI-based TFTP Clients
- 33.3 Restore Configuration
- 33.4 Uploading Firmware and Configuration Files
- System Maintenance
- Remote Management
- Call Scheduling
- Troubleshooting
- 37.1 Problems Starting Up the Prestige
- 37.2 Problems with the LAN Interface
- 37.3 Problems with the WAN Interface
- 37.4 Problems with Internet Access
- 37.5 Problems with the Password
- 37.6 Problems with the Web Configurator
- 37.7 Problems with a Telephone or the Telephone Port
- 37.8 Problems with Voice Service
- 37.9 Pop-up Windows, JavaScripts and Java Permissions
- Product Specifications
- Wall-mounting Instructions
- Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
- IP Subnetting
- PPPoE
- Triangle Route
- SIP Passthrough
- Index
P-2302R Series User’s Guide
91 Chapter 7 Introduction to VoIP
7.2.1.2 SIP Service Domain
The SIP service domain of the VoIP service provider is the domain name in a SIP URI. For
example, if the SIP address is 1122334455@VoIP-provider.com
, then “VoIP-provider.com” is
the SIP service domain.
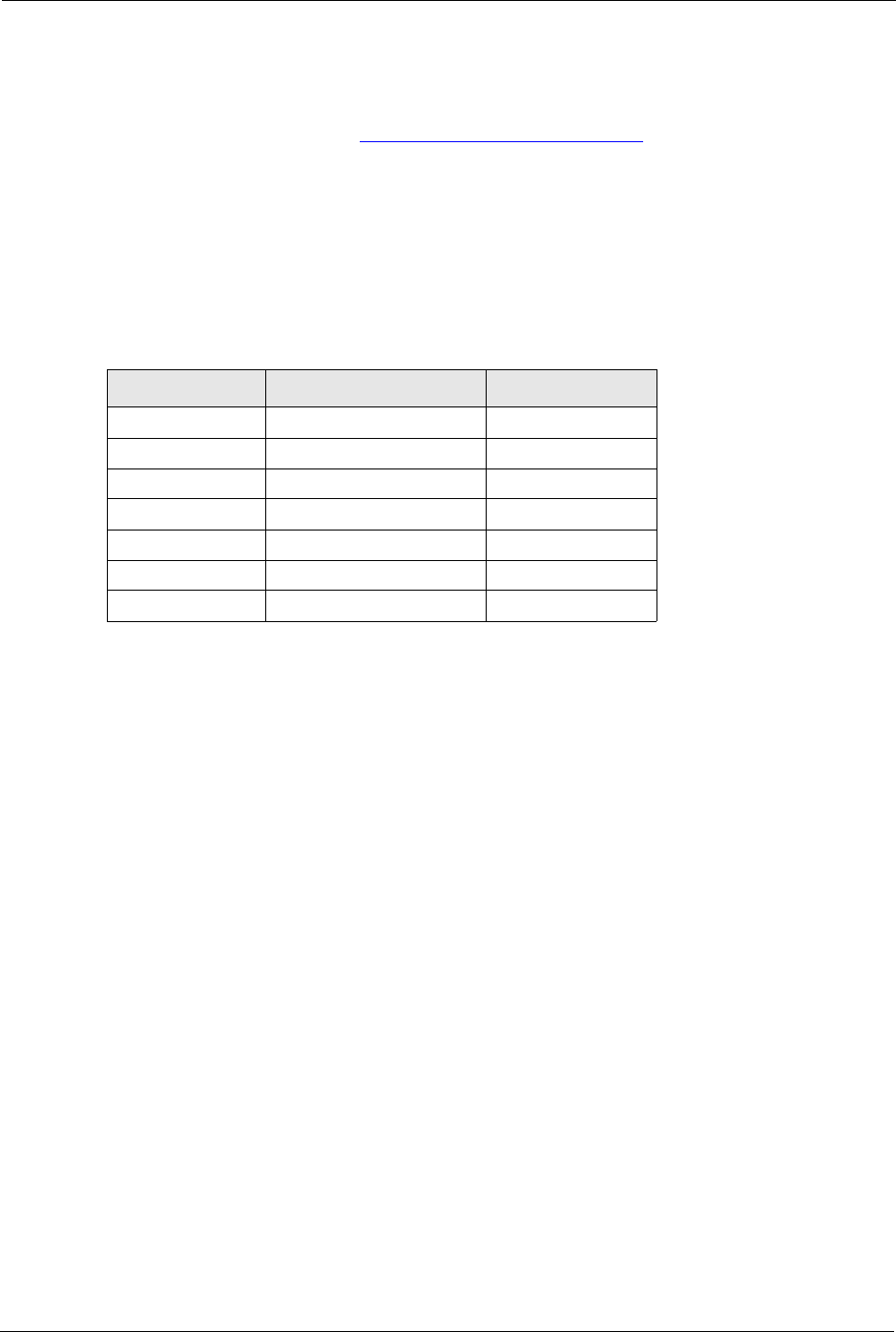
7.2.2 SIP Call Progression
The following figure displays the basic steps in the setup and tear down of a SIP call. A calls
B.
1 A sends a SIP INVITE request to B. This message is an invitation for B to participate in a
SIP telephone call.
2 B sends a response indicating that the telephone is ringing.
3 B sends an OK response after the call is answered.
4 A then sends an ACK message to acknowledge that B has answered the call.
5 Now A and B exchange voice media (talk).
6 After talking, A hangs up and sends a BYE request.
7 B replies with an OK response confirming receipt of the BYE request and the call is
terminated.
7.2.3 SIP Client Server
SIP is a client-server protocol. A SIP client is an application program or device that sends SIP
requests. A SIP server responds to the SIP requests.
When you use SIP to make a VoIP call, it originates at a client and terminates at a server. A
SIP client could be a computer or a SIP phone. One device can act as both a SIP client and a
SIP server.
Table 19 SIP Call Progression
A B
1. INVITE
2. Ringing
3. OK
4. ACK
5.Dialogue (voice traffic)
6. BYE
7. OK










