802.11g HomePlug AV ADSL2+ Gateway User's Guide
Table Of Contents
- User’s Guide
- Introduction
- Introducing the P-660HWP-Dx
- Introducing the Web Configurator
- 2.1 Web Configurator Overview
- 2.2 Accessing the Web Configurator
- 2.2.1 User Access
- 2.2.2 Administrator Access
- 2.3 Resetting the P-660HWP-Dx
- 2.3.1 Using the Reset Button
- 2.4 Navigating the Web Configurator
- 2.4.1 Navigation Panel
- 2.4.2 Status Screen
- 2.4.3 Status: Any IP Table
- 2.4.4 Status: WLAN Status
- 2.4.5 Status: Bandwidth Status
- 2.4.6 Status: Powerline Statistics
- 2.4.7 Status: Packet Statistics
- 2.4.8 Changing Login Password
- Wizards
- Network
- WAN Setup
- 5.1 WAN Overview
- 5.1.1 Encapsulation
- 5.1.2 Multiplexing
- 5.1.3 Encapsulation and Multiplexing Scenarios
- 5.1.4 VPI and VCI
- 5.1.5 IP Address Assignment
- 5.1.6 Nailed-Up Connection (PPP)
- 5.1.7 NAT
- 5.2 Metric
- 5.3 Traffic Shaping
- 5.3.1 ATM Traffic Classes
- 5.4 Zero Configuration Internet Access
- 5.5 Internet Connection
- 5.5.1 Configuring Advanced Internet Connection Setup
- 5.6 Configuring More Connections
- 5.6.1 More Connections Edit
- 5.6.2 Configuring More Connections Advanced Setup
- 5.7 Traffic Redirect
- 5.8 Configuring WAN Backup
- LAN Setup
- 6.1 LAN Overview
- 6.1.1 LANs, WANs and the P-660HWP-Dx
- 6.1.2 DHCP Setup
- 6.1.3 DNS Server Address
- 6.1.4 DNS Server Address Assignment
- 6.2 LAN TCP/IP
- 6.2.1 IP Address and Subnet Mask
- 6.2.2 RIP Setup
- 6.2.3 Multicast
- 6.2.4 Any IP
- 6.3 Configuring LAN IP
- 6.3.1 Configuring Advanced LAN Setup
- 6.4 DHCP Setup
- 6.5 LAN Client List
- 6.6 LAN IP Alias
- Wireless LAN
- 7.1 Wireless Network Overview
- 7.2 Wireless Network Setup
- 7.2.1 Requirements
- 7.2.2 Setup Information
- 7.3 Wireless Security Overview
- 7.3.1 SSID
- 7.3.2 MAC Address Filter
- 7.3.3 User Authentication
- 7.3.4 Encryption
- 7.3.5 One-Touch Intelligent Security Technology (OTIST)
- 7.4 General Wireless LAN Screen
- 7.4.1 No Security
- 7.4.2 WEP Encryption
- 7.4.3 WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
- 7.4.4 WPA/WPA2
- 7.4.5 Wireless LAN Advanced Setup
- 7.5 OTIST
- 7.5.1 Enabling OTIST
- 7.5.2 Starting OTIST
- 7.5.3 Notes on OTIST
- 7.6 MAC Filter
- 7.7 WMM QoS
- 7.7.1 WMM QoS Example
- 7.7.2 WMM QoS Priorities
- 7.7.3 Services
- 7.8 QoS Screen
- 7.8.1 ToS (Type of Service) and WMM QoS
- 7.8.2 Application Priority Configuration
- Powerline
- Network Address Translation (NAT)
- 9.1 NAT Overview
- 9.1.1 NAT Definitions
- 9.1.2 What NAT Does
- 9.1.3 How NAT Works
- 9.1.4 NAT Application
- 9.1.5 NAT Mapping Types
- 9.2 SUA (Single User Account) Versus NAT
- 9.3 SIP ALG
- 9.4 NAT General Setup
- 9.5 Port Forwarding
- 9.5.1 Default Server IP Address
- 9.5.2 Port Forwarding: Services and Port Numbers
- 9.5.3 Configuring Servers Behind Port Forwarding (Example)
- 9.6 Configuring Port Forwarding
- 9.6.1 Port Forwarding Rule Edit
- 9.7 Address Mapping
- 9.7.1 Address Mapping Rule Edit
- WAN Setup
- Security
- Firewalls
- 10.1 Firewall Overview
- 10.2 Types of Firewalls
- 10.2.1 Packet Filtering Firewalls
- 10.2.2 Application-level Firewalls
- 10.2.3 Stateful Inspection Firewalls
- 10.3 Introduction to ZyXEL’s Firewall
- 10.3.1 Denial of Service Attacks
- 10.4 Denial of Service
- 10.4.1 Basics
- 10.4.2 Types of DoS Attacks
- 10.5 Stateful Inspection
- 10.5.1 Stateful Inspection Process
- 10.5.2 Stateful Inspection and the P-660HWP-Dx
- 10.5.3 TCP Security
- 10.5.4 UDP/ICMP Security
- 10.5.5 Upper Layer Protocols
- 10.6 Guidelines for Enhancing Security with Your Firewall
- 10.6.1 Security In General
- 10.7 Packet Filtering Vs Firewall
- 10.7.1 Packet Filtering:
- 10.7.2 Firewall
- Firewall Configuration
- 11.1 Access Methods
- 11.2 Firewall Policies Overview
- 11.3 Rule Logic Overview
- 11.3.1 Rule Checklist
- 11.3.2 Security Ramifications
- 11.3.3 Key Fields For Configuring Rules
- 11.4 Connection Direction
- 11.4.1 LAN to WAN Rules
- 11.4.2 Alerts
- 11.5 General Firewall Policy
- 11.6 Firewall Rules Summary
- 11.6.1 Configuring Firewall Rules
- 11.6.2 Customized Services
- 11.6.3 Configuring a Customized Service
- 11.7 Example Firewall Rule
- 11.8 Predefined Services
- 11.9 Anti-Probing
- 11.10 DoS Thresholds
- 11.10.1 Threshold Values
- 11.10.2 Half-Open Sessions
- 11.10.3 Configuring Firewall Thresholds
- Content Filtering
- Certificates
- 13.1 Certificates Overview
- 13.1.1 Advantages of Certificates
- 13.2 Self-signed Certificates
- 13.3 Verifying a Certificate
- 13.3.1 Checking the Fingerprint of a Certificate on Your Computer
- 13.4 Configuration Summary
- 13.5 My Certificates
- 13.6 My Certificates > Details
- 13.7 My Certificates > Create
- 13.8 My Certificates > Import
- 13.8.1 Certificate File Formats
- 13.9 Trusted CAs
- 13.10 Trusted CA Details
- 13.11 Trusted CA > Import
- 13.12 Trusted Remote Hosts
- 13.13 Trusted Remote Hosts > Import
- 13.14 Trusted Remote Host Certificate Details
- 13.15 Directory Servers
- 13.16 Directory Server Add or Edit
- Firewalls
- Advanced
- Static Route
- Bandwidth Management
- 15.1 Bandwidth Management Overview
- 15.2 Application-based Bandwidth Management
- 15.3 Subnet-based Bandwidth Management
- 15.4 Application and Subnet-based Bandwidth Management
- 15.5 Scheduler
- 15.5.1 Priority-based Scheduler
- 15.5.2 Fairness-based Scheduler
- 15.6 Maximize Bandwidth Usage
- 15.6.1 Reserving Bandwidth for Non-Bandwidth Class Traffic
- 15.6.2 Maximize Bandwidth Usage Example
- 15.6.3 Bandwidth Management Priorities
- 15.7 Over Allotment of Bandwidth
- 15.8 Configuring Summary
- 15.9 Bandwidth Management Rule Setup
- 15.10 DiffServ
- 15.10.1 DSCP and Per-Hop Behavior
- 15.10.2 Rule Configuration
- 15.11 Bandwidth Monitor
- Dynamic DNS Setup
- Remote Management Configuration
- 17.1 Remote Management Overview
- 17.1.1 Remote Management Limitations
- 17.1.2 Remote Management and NAT
- 17.1.3 System Timeout
- 17.2 WWW
- 17.3 Telnet
- 17.4 Configuring Telnet
- 17.5 Configuring FTP
- 17.6 SNMP
- 17.6.1 Supported MIBs
- 17.6.2 SNMP Traps
- 17.6.3 Configuring SNMP
- 17.7 Configuring DNS
- 17.8 Configuring ICMP
- 17.9 TR-069
- Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
- 18.1 Introducing Universal Plug and Play
- 18.1.1 How do I know if I'm using UPnP?
- 18.1.2 NAT Traversal
- 18.1.3 Cautions with UPnP
- 18.2 UPnP and ZyXEL
- 18.2.1 Configuring UPnP
- 18.3 Installing UPnP in Windows Example
- 18.3.1 Installing UPnP in Windows Me
- 18.3.2 Installing UPnP in Windows XP
- 18.4 Using UPnP in Windows XP Example
- 18.4.1 Auto-discover Your UPnP-enabled Network Device
- 18.4.2 Web Configurator Easy Access
- Maintenance and Troubleshooting
- Appendices and Index
Chapter 5 WAN Setup
P-660HWP-Dx User’s Guide
39
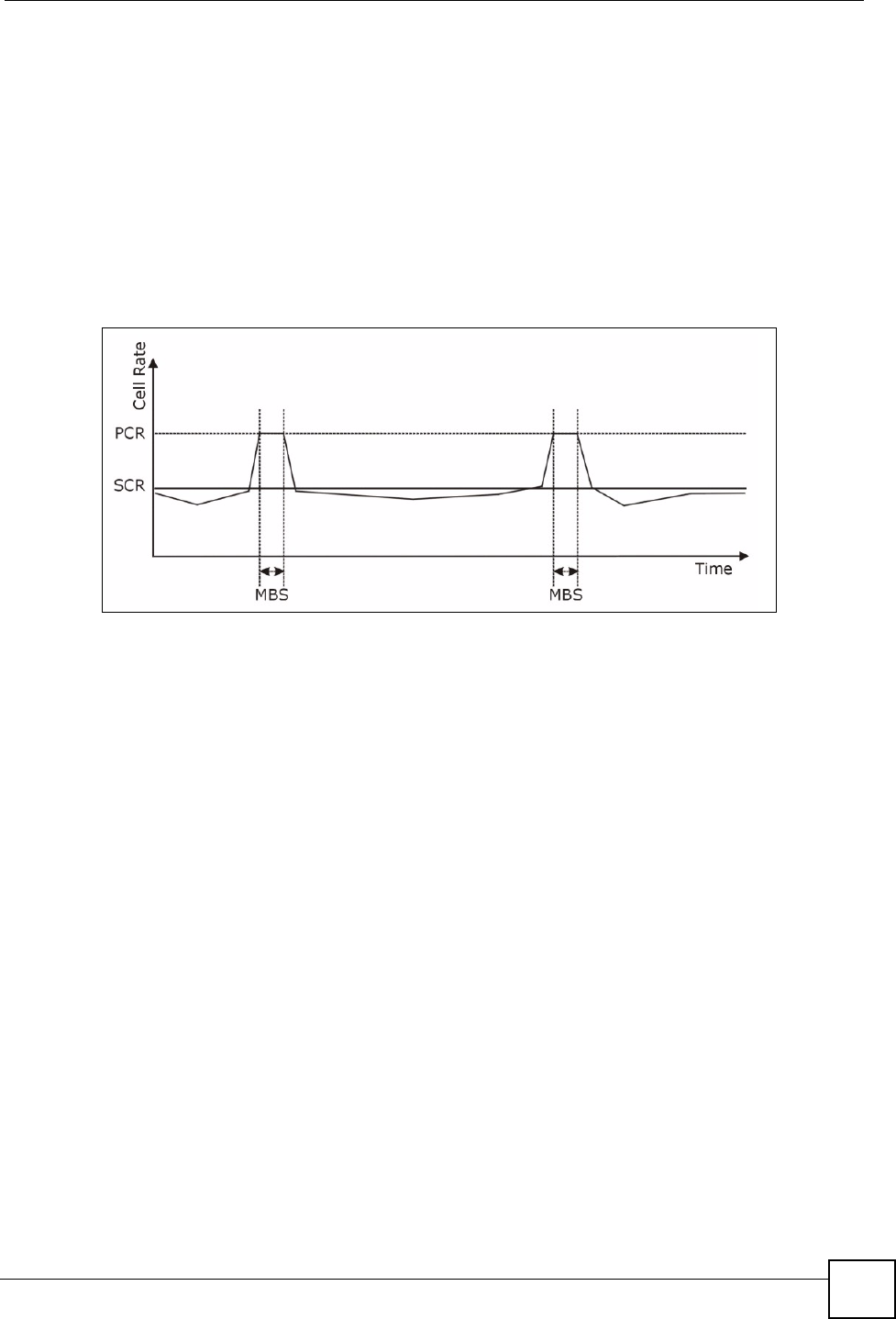
Sustained Cell Rate (SCR) is the mean cell rate of each bursty traffic source. It specifies the
maximum average rate at which cells can be sent over the virtual connection. SCR may not be
greater than the PCR.
Maximum Burst Size (MBS) is the maximum number of cells that can be sent at the PCR.
After MBS is reached, cell rates fall below SCR until cell rate averages to the SCR again. At
this time, more cells (up to the MBS) can be sent at the PCR again.
If the PCR, SCR or MBS is set to the default of "0", the system will assign a maximum value
that correlates to your upstream line rate.
The following figure illustrates the relationship between PCR, SCR and MBS.
Figure 44 Example of Traffic Shaping
5.3.1 ATM Traffic Classes
These are the basic ATM traffic classes defined by the ATM Forum Traffic Management 4.0
Specification.
5.3.1.1 Constant Bit Rate (CBR)
Constant Bit Rate (CBR) provides fixed bandwidth that is always available even if no data is
being sent. CBR traffic is generally time-sensitive (doesn't tolerate delay). CBR is used for
connections that continuously require a specific amount of bandwidth. A PCR is specified and
if traffic exceeds this rate, cells may be dropped. Examples of connections that need CBR
would be high-resolution video and voice.
5.3.1.2 Variable Bit Rate (VBR)
The Variable Bit Rate (VBR) ATM traffic class is used with bursty connections. Connections
that use the Variable Bit Rate (VBR) traffic class can be grouped into real time (VBR-RT) or
non-real time (VBR-nRT) connections.
The VBR-RT (real-time Variable Bit Rate) type is used with bursty connections that require
closely controlled delay and delay variation. It also provides a fixed amount of bandwidth (a
PCR is specified) but is only available when data is being sent. An example of an VBR-RT
connection would be video conferencing. Video conferencing requires real-time data transfers
and the bandwidth requirement varies in proportion to the video image's changing dynamics.










