User's Manual
©WhereNet Corp. TFF-2000-00AA_WhereTag IV Users Guide Page 4
Introduction
System overview
The WhereNet Real Time Locating System (RTLS) is designed to permit users to determine the position of tagged assets
in both indoor and outdoor facilities such as factories and freight yards. The system locates tagged assets by a process
involving redundant triangulation. Each tag autonomously emits a 2.4 GHz direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) radio
signal at predetermined blink rate. Each tag’s blink rate is randomized around its predetermined value to minimize the
number of collisions between transmissions made by different tags. The signal emitted by the tag is received by a
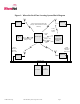
minimum of four Location Antennas. A typical transmission contains a preamble which is used to synchronize the
receiver, the tag’s serial number which identifies the tag, a status word which monitors various tag functions, data stored
in the tag’s memory and finally a CRC used to assure that the tag’s message is correct as received.
The principal components of WhereNet’s RTLS are shown in Figure 1.
WhereTag IV Device
The WhereTag IV is a key component of the WhereNet Real Time Locating System (RTLS). It is a small device that can
be attached to assets of many kinds, such as forklifts, containers, ULDs, hospital and test equipment as well as trailers and
container chassis's. It is used to manage those assets by allowing them to be identified and located by the system.
The WhereTag IV "blinks" an RF transmission at pre-programmed rates ranging from 0.5 seconds to one hour between
blinks. The WhereNet RTLS infrastructure receives these blinks and use sophisticated Differential Time of Arrival,
(DTOA), algorithms to determine the location of the tag. Accuracy of this determined location can be as low as 2 meters
and is nominally within 3 meters in most installations.
The WhereTag IV complies with the ISO 24730-2 RTLS standard. It operates in the globally accepted 2.4GHz frequency
band and transmits spread spectrum signals in accordance with the standard. The use of direct sequence spread spectrum
technology provides extremely long range; in excess of 1,000 meter locate range outdoors, and 300 meter locate range
indoors.
The WhereTag IV also incorporates an 802.11b transceiver for data communication and/or positioning by standard or
location-enabling 802.11 access points.
The combination of low average power consumption and good engineering allow the WhereTag IV to operate for long
periods of time without any maintenance. Battery life can be a long as 7 years depending upon blink rate.
A magnetic receiver is also built into the WhereTag IV. The tag can receive low frequency magnetic signals from an
exciter called a WherePort. The WherePort transmissions can be read at distances ranging from 1 to 7 meters.
Each WhereTag IV has a unique identification number that is transmitted via radio during each blink. When its battery is
running low, the tag alerts the WhereNet RTLS infrastructure so that the tag can be proactively replaced. WhereTag IVs
are configured with WhereNet’s WhereWand.
The WhereTag unique ID number is also printed as a Code 128 on the bar code labels affixed to the tag’s case. The bar
code enables seamless integration with existing inventory systems and delivers a cost effective total resource visibility
solution that extends beyond the range of the WhereNet RTLS.
Designed to operate in a wide range of applications, the WhereTag IV is fully sealed and will function in both indoor and
outdoor environments. The tag's case is also resistant to oils, solvents and hydraulic fluids.