User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Preface
- Introduction
- Printer Setup
- Printer Operation
- Front Panel Controls
- RFID Guidelines
- Overview
- Getting Started with RFID
- Creating Basic RFID Label Formats
- RFID Label Format 1-Write a 96-bit Tag in Hexadecimal
- RFID Label Format 2-Write a 64-bit Tag in Hexadecimal
- RFID Label Format 3-Write a 96-bit Tag in ASCII
- RFID Label Format 4-Read Data from Tag and Print on Label
- RFID Label Format 5-Write Tag, Read Tag, and Print Data on Label
- RFID Label Format 6-Write Tag, Read Tag, and Return Results to Host
- ZPL II Commands for RFID
- Data Ports
- Memory Cards
- Routine Maintenance
- Troubleshooting
- Specifications
- Proprietary Statement
- Warranty Information
- Printer Software and Firmware License Agreement
- Index
14 R110Xi/R170Xi User Guide 23063L-003 Rev. A 6/24/05
Printer Setup
Types of Media
Types of Media
The printer can use various types of media (Table 4). We strongly recommend the use of
Zebra-brand supplies for continuous high-quality printing. A wide range of paper,
polypropylene, polyester, and vinyl stock has been specifically engineered to enhance the
printing capabilities of the printer and to ensure against premature printhead wear.
Table 4 • Types of Media
Media Type How It Looks Description
Non-Continuous
Roll Media
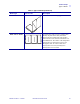
The media is wound on a core. Individual labels
are separated by a gap, black mark, notch, or
hole, which enables you to see where one label
ends and the next one begins. When using media
that has holes or notches, position the media
sensor directly over a hole or notch. Figure 9
shows different types of non-continuous media.
Figure 9 • Non-Continuous Web Media
Continuous
Roll Media
The media is wound on a core and is without
gaps, holes, notches, or black marks. This allows
the image to be printed anywhere on the label.