User's Manual
Chapter 5 Utility Overview Page 58
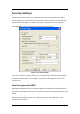
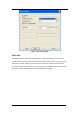
Figure 76 Security Settings
Encryption Mode
WPA improves data encryption by using Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP), Message
Integrity Check (MIC) and IEEE 802.1X. WPA2 use Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) in
the Counter mode with Cipher block chaining Message authentication code Protocol (CCMP)
to offer stronger encryption than TKIP.
The encryption mechanism used for WPA(2) and WPA(2)-PSK are the same. The only
difference between them is that WPA(2)-PSK uses a simple common password, instead of
user specific credentials. The common password approach makes WPA(2)-PSK susceptible to
brute-force password-guessing attacks but it’s still an improvement over WEP as it employs a
consistent, single, alphanumeric password to derive a PMK which is used to generate unique
temporal encryption keys.
IEEE 802.1X Authentication
WPA and WPA2 apply IEEE 802.1X and Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) to
authenticate wireless stations using an external RADIUS database. WPA2 reduces the
number of key exchange messages from six to four (CCMP 4 way handshake) and shortens
the time required to connect to a network. Other WPA2 authentication features that are
different from WPA include key caching and pre-authentication.