Manual
IM 11M12D01-01E
3-7
3. Installation
<When the surface temperature is less than 2008C or the dew point of the measure-
ment gas>
(1) When the furnace pressure is negative, raise the analyzer pressure to increase
induction flow of the measurement gas.
Refer to Section 2.6.3, Auxiliary Ejector for High-temperature Use, for the setting of
induction flow.
If there is much dust in the gas, the ejector may become clogg is induction flow
increases.
(2) When the furnace pressure is positive, open the needle valve for the sample gas
outlet to increase the gas flow.
Refer to Section 4.1.4, Piping to the High-temperature Probe Adapter.
(3) Warm the probe adapter. Refer to Section 4.2.4, Piping to the High-temperature
Probe Adapter. Ensure that its temperature does not drop below freezing point in
winter.
(4) When the surface temperature is still less than 2008C or the dew point of the mea-
surement gas, even if the above measures have been taken, warm the probe adapter
using a heat source such as steam.
3.2.3 Probe Insertion Hole
A high-temperature detector consists of a ZR22G-015 Detector and ZO21P High-
temperature Probe Adapter. When forming the probe insertion hole, the following should
be taken into consideration:
(1) If the probe is made of silicon carbide (SiC), the probe hole should be formed so that
the probe is mounted vertically (no more than a 58 tilt).
(2) In the case where the probe is made of stainless steel and the probe adapter is to be
mounted horizontally, the probe hole should be formed so that the probe tip is not
higher than the probe base.
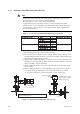
Figure 3.5 illustrates examples of the probe insertion hole.
6 8
Figure 3.5 Examples of the probe insertion hole