User manual
MyPBX Standard User Manual
www.yeastar.com Page 43
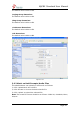
2) NAT
·External IP
Address displayed in outbound SIP messages when behind a NAT
·External Host
If you specify an external host name, MyPBX will perform DNS queries on the
host name periodically. Not recommended for production environments! Use
External IP instead.
·External Refresh
Set how often to refresh the external host if used. You may specify a local
network in the field below
·Local Network Address
'192.168.0.0/255.255.0.0' : All RFC 1918 addresses are local networks;
'10.0.0.0/255.0.0.0' : Also RFC1918;
'172.16.0.0/12':Another RFC1918 with CIDR notation;
'169.254.0.0/255.255.0.0' : Zero conf local network.
·NAT Mode
Global NAT settings (Affects all peers and users);
Yes = Always ignore info and assume NAT;
No = Use NAT mode only according to RFC3581;
Never = Never attempt NAT mode or RFC3581 support;
Route = Assume NAT, don't send report
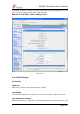
·Allow RTP Reinvite
MyPBX by default tries to redirect the RTP media stream (audio) directly from
the caller to the callee. Some devices do not support this (especially if one of
them is behind a NAT).
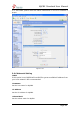
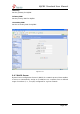
3)Codecs
A codec is a compression or decompression algorithm that used in the
transmission of voice packets over a network or the Internet.
u-law: A PSTN standard codec, used in North America, that provides very
good voice quality and consumes 64kbit/s in each direction (receiving and
transmitting) of a VoIP call.
a-law: A PSTN standard codec, used outside of North America, that
provides very good voice quality and consumes 64kbit/s in each direction
(receiving and transmitting) of a VoIP call.
GSM: A wireless standard codec, used worldwide, that provides adequate
voice quality and consumes 13.3kbit/s in each direction (receiving and
transmitting) of a VoIP call. GSM is supported by many VoIP phones.
G.726: A PSTN codec, used worldwide, that provides good voice quality and