WitMotion Shenzhen Co., Ltd| Datasheet AHRS IMU Sensor | WT901SDCL The Robust Acceleration, Angular velocity, Angle & Magnetic filed Detector The WT901SDCL is a IMU sensor device, detecting acceleration, angular velocity, angle as well as magnetic filed. The robust housing and the small outline makes it perfectly suitable for industrial applications such as condition monitoring and predictive maintenance.
Tutorial Link Google Drive Link to instructions DEMO: WITMOTION Youtube Channel WT901SDCL Playlist If you have technical problems or cannot find the information that you need in the provided documents, please contact our support team. Our engineering team is committed to providing the required support necessary to ensure that you are successful with the operation of our AHRS sensors.
Contents Tutorial Link............................................................................................................................. - 2 Contact....................................................................................................................................... - 2 Application................................................................................................................................ - 2 Contents.............................................................
5.2.16 6.2.17 6.2.18 6.2.19 Set Set Set Set Z Axis Angular Velocity Bias.................................................... X Axis Magnetic Bias................................................................... Y Axis Magnetic Bias................................................................... Z Axis Magnetic Bias................................................................... - WT901SDCL | Datasheet v20-0605 | 23 24 24 24 http://wiki.wit-motion.
1 Overview WT901SDCL’s scientific name is AHRS IMU sensor. A sensor measures 3-axis angle, angular velocity, acceleration and magnetic field. Its strength lies in the algorithm which can calculate three-axis angle accurately. WT901SDCL is employed where the highest measurement accuracy is required.
2 Features The default baud rate of this device is 9600 and could be changed. The interface of this product only leads to a serial port The module consists of a high precision gyroscope, accelerometer, geomagnetic field and barometer sensor. The product can solve the current real-time motion high-performance posture of the microprocessor, module advanced quickly dynamic by using the solutions and Kalman filter algorithm.
3 Specification 3.1 Parameter Parameter Specification Working Voltage TTL:3.3V-5V Current <25mA Battery 250mAh, 3.7V Working hour A. Play 4h at 1 charge (battery) B. Power source of 5V Size 51.3mm x 36mm X 15mm 2.02" x 1.41" x 0.59" Data Angle: X Y Z, 3-axis Acceleration: X Y Z, 3-axis Angular Velocity: X Y Z, 3-axis Magnetic Field : X Y Z, 3-axis Time, Quaternion Output frequency 0.
(Y-axis 90° is singular point) WT901SDCL | Datasheet v20-0605 | AA-(after magnetic calibration) http://wiki.wit-motion.
3.2 Size Parameter Specification Tolerance Length 51.3 ±0.1 Width 36 ±0.1 Height 15 ±0.1 Weight 18 ±1 WT901SDCL | Datasheet v20-0605 | Comment Unit: millimeter. Unit: gram http://wiki.wit-motion.
3.3 Axial Direction The coordinate system used for attitude angle settlement is the northeast sky coordinate system. Place the module in the positive direction, as shown in the figure below, direction left is the Y-axis, the direction forward is the X-axis, and direction upward is the Z-axis. Euler angle represents the rotation order of the coordinate system when the attitude is defined as Z-Y-X, that is, first turn around the Z-axis, then turn around the Y-axis, and then turn around the X-axis.
4 Port Definition Port Micro-USB SD Card Port Function 3.3-5V power charge input , TTL interface Insert the SD Card for saving data WT901SDCL | Datasheet v20-0605 | http://wiki.wit-motion.
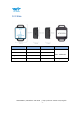
5 Casing Specification WT901SDCL | Datasheet v20-0605 | http://wiki.wit-motion.
6 Communication Protocol Level: TTL level Baud rate: 4800, 9600 (default), 19200 38400, 57600, 115200, 230400, 460800, 921600, stop bit and parity 6.1 Output Data Format 6.1.1 Time Output 0x55 0x50 YY MM DD hh mm ss msL msH SUM YY:Year, 20YY Year MM:Month DD:Day hh:hour mm:minute ss:Second ms:Millisecond Millisecond calculate formula: ms=((msH<<8)|msL) Sum=0x55+0x51+YY+MM+DD+hh+mm+ss+ms+TL WT901SDCL | Datasheet v20-0605 | http://wiki.wit-motion.
6.1.2 Acceleration Output 0x55 0x51 AxL AxH AyL AyH AzL AzH TL TH SUM Calculate formula: ax=((AxH<<8)|AxL)/32768*16g(g is Gravity acceleration, 9.8m/s2) ay=((AyH<<8)|AyL)/32768*16g(g is Gravity acceleration, 9.8m/s2) az=((AzH<<8)|AzL)/32768*16g(g is Gravity acceleration, 9.8m/s2) Temperature calculated formular: T=((TH<<8)|TL)/100 ℃ Checksum: Sum=0x55+0x51+AxH+AxL+AyH+AyL+AzH+AzL+TH+TL Note: 1. The data is sent in hexadecimal, not ASCII code.
6.1.4 Angle Output 0x55 0x53 RollL RollH PitchL PitchH YawL YawH VL VH SUM Calculated formular: Roll(X axis)Roll=((RollH<<8)|RollL)/32768*180(°) Pitch(Y axis)Pitch=((PitchH<<8)|PitchL)/32768*180(°) Yaw(Z axis)Yaw=((YawH<<8)|YawL)/32768*180(°) Version calculated formula: Version=(VH<<8)|VL Checksum: Sum=0x55+0x53+RollH+RollL+PitchH+PitchL+YawH+YawL+VH+VL Note: 1. The coordinate system used for attitude angle settlement is the northeast sky coordinate system.
6.1.5 Magnetic Output 0x55 0x54 HxL HxH HyL HyH HzL HzH TL TH SUM Q3H SUM Calculated formular: Magnetic(x axis)Hx=(( HxH<<8)| HxL) Magnetic(y axis)Hy=(( HyH <<8)| HyL) Magnetic(z axis)Hz =(( HzH<<8)| HzL) Temperature calculated formular: T=((TH<<8)|TL) /100℃ Checksum: Sum=0x55+0x53+HxH+HxL+HyH+HyL+HzH+HzL+TH+TL 6.1.
6.2 Config Commands Reminder: 1. Data format 0xFF 0xAA Address DataL DataH 6.2.
0x3f Yaw Z axis Angle 0x40 TEMP Temperature 0x51 Q0 Quaternion Q0 0x52 Q1 Quaternion Q1 0x53 Q2 Quaternion Q2 0x54 Q3 Quaternion Q3 6.2.2 Save Configuration 0xFF 0xAA 0x00 SAVE:Save 0:Save current configuration 1:set to default setting SAVE 0x00 CALSW 0x00 6.2.3 Calibrate 0xFF 0xAA 0x01 CALSW:Set calibration mode 0:Exit calibration mode 1:Enter Gyroscope and Accelerometer calibration mode 2:Enter magnetic calibration mode 6.2.
6.2.5 Sleep/ Wake up 0xFF 0xAA 0x22 0x01 0x00 After sending the command, the module enters the sleep (standby) state, and once again, the module enters the working state from the standby state. 6.2.6 Algorithm Transition 0xFF 0xAA 0x24 ALG 0x00 ALG:6-axis/ 9-axis algorithm transition 0:switch to 9-axis algorithm 1:switch to 6-axis algorithm 6.2.
6.2.8 Return Content 0xFF 0xAA RSWL byte definition byte 7 6 0x02 5 RSWL 4 RSWH 3 2 1 0 Name 0x57 pack 0x56 pack 0x55 pack 0x54 pack 0x53 pack 0x52 pack 0x51 pack 0x50 pack default 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 RSWH byte definition byte 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Name X X X X X 0x5A pack 0x59 pack 0x58 pack default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 X is an undefined value.
6.2.9 Return Rate 0xFF 0xAA 0x03 RATE 0x00 RATE:return rate 0x01 :0.2Hz 0x02:0.5Hz 0x03:1Hz 0x04:2Hz 0x05:5Hz 0x06:10Hz(default) 0x07:20Hz 0x08:50Hz 0x09:100Hz 0x0a:125Hz 0x0b:200Hz 0x0c:Single 0x0d: Not output After the setup is complete, need to click save, and re-power the module to take effect. 6.2.
6.2.11 Set X Axis Acceleration Bias 0xFF 0xAA 0x05 AXOFFSETL AXOFFSETH AXOFFSETL:X axis Acceleration bias low byte AXOFFSETH:X axis Acceleration bias high byte AXOFFSET= (AXOFFSETH <<8) | AXOFFSETL Note:After setting the acceleration bias, the output value of the acceleration is the sensor measured value minus the bias value. 6.2.
6. 2.14 Set X Axis Angular Velocity Bias 0xFF 0xAA 0x08 GXOFFSETL GXOFFSETH GXOFFSETL:Set X axis Angular velocity bias low byte GXOFFSETH:Set Y axis Angular velocity bias high byte GXOFFSET= (GXOFFSETH <<8) | GXOFFSETL Note:After setting the angular velocity zero deviation, the output value of the angular velocity is the sensor measurement value minus the zero deviation value. 6.2.
6.2.17 Set X Axis Magnetic Bias 0xFF 0xAA 0x0b HXOFFSETL HXOFFSETH HXOFFSETL:Set X axis magnetic bias low byte HXOFFSETH:Set X axis magnetic bias high byte HXOFFSET= (HXOFFSETH <<8) | HXOFFSETL Note:After setting the magnetic field bias, the output value of the magnetic field is the sensor measured value minus the zero bias value. 6.2.