User guide
WML Linux Thin Client User Guide
VNC – TightVNC
VNC is a well established protocol for providing access to a graphical computer session via a
network. VNC servers are available for Unix/Linux and Windows computers.
The WML Linux Thin Client ships with the TightVNC vnc viewer program, which extends the VNC
protocol adding extra compression to the connection, by using JPEG image compression – the
original VNC protocol sent uncompressed bitmap images over the network.
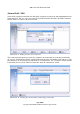
Open a new connection and choose “VNC (tightvnc)” from the drop down menu.
“Connection name” and “Server” are used to identify the connection and control which server to
connect to. Like RDP, SSH, telnet and NX connections, the port can be configured, but with VNC, an
alternative to specifying the port is to specify the display number. Illustration 31 shows a user
changing from port to display.
The “Username” field is optional, some VNC servers will not require a username.
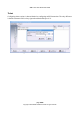
The “Encoding” field refers to image encoding. If this menu is left as “defaults” a range of image
encodings will be tried. To specify a particular encoding, select from the list. Possible encodings are:
copyrect, tight, hextile, zlib, corre, rre and raw. “tight” encoding uses JPEG compression and is the
recommended setting. This is the first encoding to be tried if “defaults” is selected.
“Image quality” is used to specify the amount of JPEG compression used if “tight” encoding is
chosen.
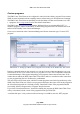
The “Fullscreen” checkbox determines whether the session will run fullscreen or in a managed
window.
page 34/62
Copyright © 2008 William Matthew Limited. All rights reserved
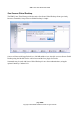
Illustration 31: Configuring a VNC connection