User Documentation
Table Of Contents
- Content
- 1 About this documentation
- 2 Safety
- 3 IO-Link overview
- 4 Module description
- 5 Assembly and installation
- 6 Commissioning
- 6.1 Requirements
- 6.2 Device description files
- 6.3 Procedure for commissioning
- 6.4 Commissioning with the SIMATIC Manager (PROFINET)
- 6.5 Commissioning with the TIA portal(PROFINET)
- 6.6 Commissioning with TwinCAT (EtherCAT)
- 6.7 Commissioning with Studio 5000(Ethernet/IP)
- 6.8 Commissioning with Automation Studio (POWERLINK)
- 6.9 Reading and writing data objects on IO-Link devices
- 6.10 “IO_LINK_CALL” function block
- 6.11 I&M functions
- 7 Planning IO-Link device configurations
- 8 Process data
- 9 Diagnostics and troubleshooting
- 10 Disassembly and disposal
6 Commissioning | Reading and writing data objects on IO-Link devices
35Manual Communication module UR20-4COM-IO-LINK2547720000/03/09.2019
6.9 Reading and writing data objects on
IO-Link devices
Protocol for acyclic accesses
If you want to read and write IO-Link data objects
only during commissioning, we recommend us-
ing the IO-Link Congurator (see Chapter 7).
In order to access data objects for a eld device (FD),
e.g.those of a IO-Link device, you must create a client appli-
cation (client app) for the eldbus master (FB_M). This client
application communicates with a server on the u-remote
station (FBC/IO_M). The server communicates with the eld
device application (FD app) on the eld device.
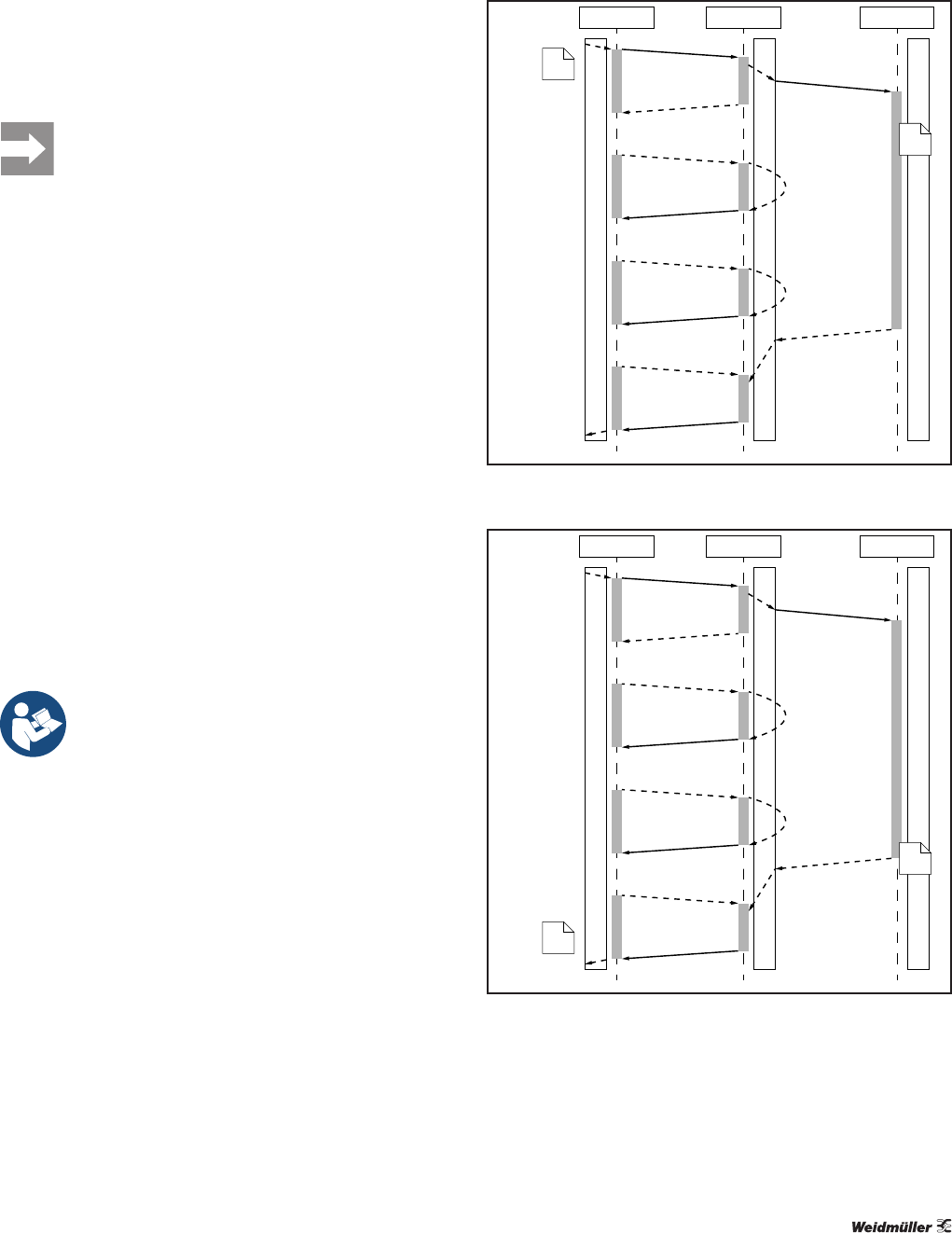
An acyclic access to an IO-Link device always begins with
a write access by the client application to the server (acy-
clic-write.req). The data written determine which request is
sent by the server to the IO-Link device application (write.req
oder read.req).
The client application then performs a sequence of read ac-
cesses (acyclic-read.req). Provided that the IO-Link device ap-
plication has not yet processed the request, the server feeds
back that the IO-Link device application is busy (acyclic-read.
res with status “Busy”). If the server has received a response
from the IO-Link device application (write.conf or read.conf),
the server then forwards the response to the client applica-
tion (acyclic-read.res with status “Done” or “Error”).
For integrating the IO-Link with PROFIBUS and
PROFINET, also refer to the integration guidelines
of the PROFIBUS user organisation.
– IO-Link Integration Part 1: Technical Specifica-
tion for PROFIBUS and PROFINET
– IO-Link Integration – Edition 2: Guideline for
PROFINET
Client app
Server
FB_M FBC/IO-M FD
FD app
data
data
write_data.res
/ with data
acyclic-read.req
acyclic-read.res
/ without data
write.conf
/ without data
/ “resource busy“
acyclic-read.req
acyclic-read.res
/ without data
/ Resource busy
/ “resource busy“
acyclic-read.req
acyclic-read.res
/ without data
/ Resource busy
acyclic-write.req
acyclic-write.res
/ without data
/ with data
write.req
/ with data
write_data.req
Writing a data object on an IO-Link device
Client app
Server
FB_M FBC/IO-M FD
FD app
data
data
read_data.res
/ with data
acyclic-read.req
acyclic-read.res
/ without data
read.conf
/ with data
/ “resource busy“
acyclic-read.req
acyclic-read.res
/ without data
/ Resource busy
/ “resource busy“
acyclic-read.req
acyclic-read.res
/ without data
/ Resource busy
acyclic-write.req
acyclic-write.res
/ without data
/ with data
read.req
/ without data
read_data.req
Reading a data object on an IO-Link device










