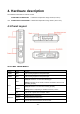
User Documentation
- 6 -
1.2 Modbus Basics
Introduction
Modbus is one of the most popular automation protocols in the world. It supports both serial and
Ethernet devices. Many industrial devices, such as PLCs, DCSs, HMIs, instruments, meters, motors,
and drivers use Modbus as their communication standard.
Devices are either Masters or Slaves
All Modbus devices are classified as either a master or a slave. Masters initiate all communication with
slaves and do not communicate to other masters. Slaves are completely passive and communicate
only
Slaves are identified by ID
Each Modbus slave in a system is assigned a unique ID between 1 and 247. Whenever a master
sends a request, the request must include the ID of the intended recipient. Master devices themselves
have no ID.
0 Broadcast address
1-247 Slave individual address
258-255 Reserved
Communication is done by Request and Response
Modbus communication generally is running by request and response. A master sends a request and
an addressed
the next request. For broadcast commands no response is expected. This is illustrated by three
scenarios as follows:
Normal communication (Peer-to-Peer)
The master sends a request to the slave. The slave sends a response with the requested information.