User Manual
Power Amplifier Serial I/F Spec.
6 Version 1.62
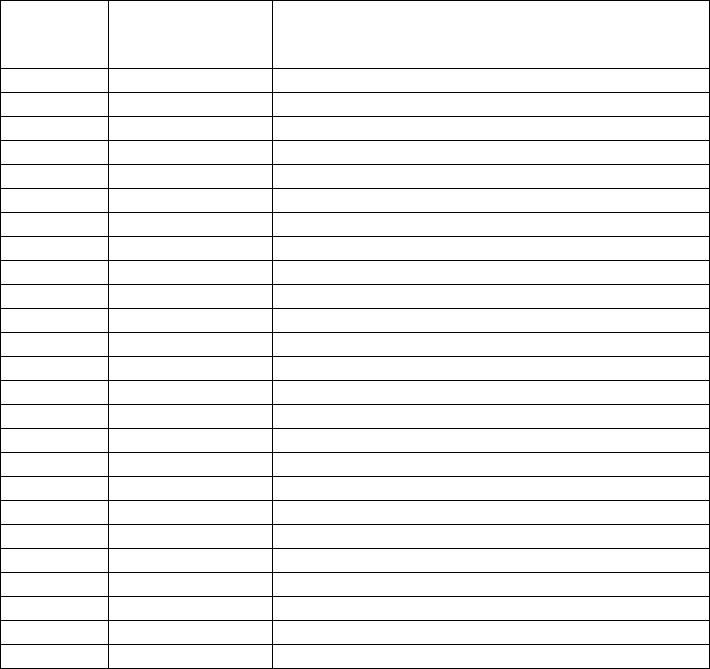
0Table 2-2
3. Microprocessor Interface
The microprocessor interface provides serial communication between the Power Amplifier and
external microprocessor/microcontroller (host). Through this interface, the Power Amplifier will
send information to the host and the host will send information to the Power Amplifier. The SPI
interface is a standard CPU interface, common on PIC and Motorola CPUs. As a point of
reference, the 68HC11 CPU is the classic implementation of the SPI, and is the reference used at
Sonik for the operation of the SPI bus.
Along with the SPI signals, there are 6 address lines on the SPI interface connector. These
address lines are used to determine which device on the SPI bus is being addressed, as well as
which information within the device is being addressed. The 6 address lines are split into 3
device select lines (device ID 0-7), and 3 register select lines.
3.1 SPI BUS ID
Each module on the SPI BUS will have an ID value as described in Table 3.1. When the address
lines associated with the device ID match the module’s ID, the module is to respond.
Relative
Offset
Page Address Description
0 0 940 MHz Attenuation Value
1 940 MHz Phase Value
2 Unused
3 Unused
4 1 930 MHz Attenuation Value
5 930 MHz Phase Value
. Unused
. Unused
. 2 Unused
. Unused
216 0x36 Serial Number (32 bytes starting at 0xD8)
. “
. “
. “
247 Serial Number
248 0x3E Model Number
249 Version Number
250 Unused
251 Unused
252 0x3F Unused
253 Unused
254 Unused
255 Checksum










