6.5.1
Table Of Contents
- vSphere Networking
- Contents
- About vSphere Networking
- Updated Information
- Introduction to Networking
- Setting Up Networking with vSphere Standard Switches
- Setting Up Networking with vSphere Distributed Switches
- vSphere Distributed Switch Architecture
- Create a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Upgrade a vSphere Distributed Switch to a Later Version
- Edit General and Advanced vSphere Distributed Switch Settings
- Managing Networking on Multiple Hosts on a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Tasks for Managing Host Networking on a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Add Hosts to a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Configure Physical Network Adapters on a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Migrate VMkernel Adapters to a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Create a VMkernel Adapter on a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Migrate Virtual Machine Networking to the vSphere Distributed Switch
- Use a Host as a Template to Create a Uniform Networking Configuration on a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Remove Hosts from a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Managing Networking on Host Proxy Switches
- Distributed Port Groups
- Working with Distributed Ports
- Configuring Virtual Machine Networking on a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Topology Diagrams of a vSphere Distributed Switch in the vSphere Web Client
- Setting Up VMkernel Networking
- VMkernel Networking Layer
- View Information About VMkernel Adapters on a Host
- Create a VMkernel Adapter on a vSphere Standard Switch
- Create a VMkernel Adapter on a Host Associated with a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Edit a VMkernel Adapter Configuration
- Overriding the Default Gateway of a VMkernel Adapter
- Configure the VMkernel Adapter Gateway by Using ESXCLI
- View TCP/IP Stack Configuration on a Host
- Change the Configuration of a TCP/IP Stack on a Host
- Create a Custom TCP/IP Stack
- Remove a VMkernel Adapter
- LACP Support on a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Convert to the Enhanced LACP Support on a vSphere Distributed Switch
- LACP Teaming and Failover Configuration for Distributed Port Groups
- Configure a Link Aggregation Group to Handle the Traffic for Distributed Port Groups
- Edit a Link Aggregation Group
- Enable LACP 5.1 Support on an Uplink Port Group
- Limitations of the LACP Support on a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Backing Up and Restoring Networking Configurations
- Rollback and Recovery of the Management Network
- Networking Policies
- Applying Networking Policies on a vSphere Standard or Distributed Switch
- Configure Overriding Networking Policies on Port Level
- Teaming and Failover Policy
- VLAN Policy
- Security Policy
- Traffic Shaping Policy
- Resource Allocation Policy
- Monitoring Policy
- Traffic Filtering and Marking Policy
- Traffic Filtering and Marking on a Distributed Port Group or Uplink Port Group
- Enable Traffic Filtering and Marking on a Distributed Port Group or Uplink Port Group
- Mark Traffic on a Distributed Port Group or Uplink Port Group
- Filter Traffic on a Distributed Port Group or Uplink Port Group
- Working with Network Traffic Rules on a Distributed Port Group or Uplink Port Group
- Disable Traffic Filtering and Marking on a Distributed Port Group or Uplink Port Group
- Traffic Filtering and Marking on a Distributed Port or Uplink Port
- Enable Traffic Filtering and Marking on a Distributed Port or Uplink Port
- Mark Traffic on a Distributed Port or Uplink Port
- Filter Traffic on a Distributed Port or Uplink Port
- Working with Network Traffic Rules on a Distributed Port or Uplink Port
- Disable Traffic Filtering and Marking on a Distributed Port or Uplink Port
- Qualifying Traffic for Filtering and Marking
- Traffic Filtering and Marking on a Distributed Port Group or Uplink Port Group
- Manage Policies for Multiple Port Groups on a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Port Blocking Policies
- Isolating Network Traffic by Using VLANs
- Managing Network Resources
- DirectPath I/O
- Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV)
- SR-IOV Support
- SR-IOV Component Architecture and Interaction
- vSphere and Virtual Function Interaction
- DirectPath I/O vs SR-IOV
- Configure a Virtual Machine to Use SR-IOV
- Networking Options for the Traffic Related to an SR-IOV Enabled Virtual Machine
- Using an SR-IOV Physical Adapter to Handle Virtual Machine Traffic
- Enabling SR-IOV by Using Host Profiles or an ESXCLI Command
- Virtual Machine That Uses an SR-IOV Virtual Function Fails to Power On Because the Host Is Out of Interrupt Vectors
- Remote Direct Memory Access for Virtual Machines
- Jumbo Frames
- TCP Segmentation Offload
- Enable or Disable Software TSO in the VMkernel
- Determine Whether TSO Is Supported on the Physical Network Adapters on an ESXi Host
- Enable or Disable TSO on an ESXi Host
- Determine Whether TSO Is Enabled on an ESXi Host
- Enable or Disable TSO on a Linux Virtual Machine
- Enable or Disable TSO on a Windows Virtual Machine
- Large Receive Offload
- Enable Hardware LRO for All VMXNET3 Adapters on an ESXi Host
- Enable or Disable Software LRO for All VMXNET3 Adapters on an ESXi Host
- Determine Whether LRO Is Enabled for VMXNET3 Adapters on an ESXi Host
- Change the Size of the LRO Buffer for VMXNET 3 Adapters
- Enable or Disable LRO for All VMkernel Adapters on an ESXi Host
- Change the Size of the LRO Buffer for VMkernel Adapters
- Enable or Disable LRO on a VMXNET3 Adapter on a Linux Virtual Machine
- Enable or Disable LRO on a VMXNET3 Adapter on a Windows Virtual Machine
- Enable LRO Globally on a Windows Virtual Machine
- NetQueue and Networking Performance
- vSphere Network I/O Control
- About vSphere Network I/O Control Version 3
- Upgrade Network I/O Control to Version 3 on a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Enable Network I/O Control on a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Bandwidth Allocation for System Traffic
- Bandwidth Allocation for Virtual Machine Traffic
- About Allocating Bandwidth for Virtual Machines
- Bandwidth Allocation Parameters for Virtual Machine Traffic
- Admission Control for Virtual Machine Bandwidth
- Create a Network Resource Pool
- Add a Distributed Port Group to a Network Resource Pool
- Configure Bandwidth Allocation for a Virtual Machine
- Configure Bandwidth Allocation on Multiple Virtual Machines
- Change the Quota of a Network Resource Pool
- Remove a Distributed Port Group from a Network Resource Pool
- Delete a Network Resource Pool
- Move a Physical Adapter Out the Scope of Network I/O Control
- Working with Network I/O Control Version 2
- MAC Address Management
- Configuring vSphere for IPv6
- Monitoring Network Connection and Traffic
- Capturing and Tracing Network Packets by Using the pktcap-uw Utility
- pktcap-uw Command Syntax for Capturing Packets
- pktcap-uw Command Syntax for Tracing Packets
- pktcap-uw Options for Output Control
- pktcap-uw Options for Filtering Packets
- Capturing Packets by Using the pktcap-uw Utility
- Trace Packets by Using the pktcap-uw Utility
- Configure the NetFlow Settings of a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Working With Port Mirroring
- vSphere Distributed Switch Health Check
- Switch Discovery Protocol
- Capturing and Tracing Network Packets by Using the pktcap-uw Utility
- Configuring Protocol Profiles for Virtual Machine Networking
- Multicast Filtering
- Stateless Network Deployment
- Networking Best Practices
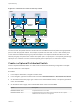
Figure 3‑3. Packet Flow on the Host Proxy Switch
VMkernel
network
Uplink port group
VM network
Host 1
0 1 3
vmnic0 vmnic1
5 6 7
Host Proxy
Switch
vmnic2
VM2 vmknic1VM1
Physical Switch
On the host side, the packet flow from virtual machines and VMkernel services passes through particular
ports to reach the physical network. For example, a packet sent from VM1 on Host 1 first reaches port 0
on the VM network distributed port group. Because Uplink 1 and Uplink 2 handle the traffic for the VM
network port group, the packet can continue from uplink port 5 or uplink port 6 . If the packet goes through
uplink port 5, it continues to vmnic0, and if the packet goes to uplink port 6, it continues to vmnic1.
Create a vSphere Distributed Switch
Create a vSphere distributed switch on a data center to handle the networking configuration of multiple
hosts at a time from a central place.
Procedure
1 In the vSphere Web Client, navigate to a data center.
2 In the navigator, right-click the data center and select Distributed Switch > New Distributed Switch.
3 On the Name and location page, type a name for the new distributed switch, or accept the generated
name, and click Next.
4 On the Select version page, select a distributed switch version and click Next.
Option Description
Distributed Switch: 6.5.0 Compatible with ESXi 6.5 and later.
Distributed Switch: 6.0.0 Compatible with ESXi 6.0 and later. Features released with later vSphere
distributed switch versions are not supported.
vSphere Networking
VMware, Inc. 30