6.5.1
Table Of Contents
- vSphere Networking
- Contents
- About vSphere Networking
- Updated Information
- Introduction to Networking
- Setting Up Networking with vSphere Standard Switches
- Setting Up Networking with vSphere Distributed Switches
- vSphere Distributed Switch Architecture
- Create a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Upgrade a vSphere Distributed Switch to a Later Version
- Edit General and Advanced vSphere Distributed Switch Settings
- Managing Networking on Multiple Hosts on a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Tasks for Managing Host Networking on a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Add Hosts to a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Configure Physical Network Adapters on a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Migrate VMkernel Adapters to a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Create a VMkernel Adapter on a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Migrate Virtual Machine Networking to the vSphere Distributed Switch
- Use a Host as a Template to Create a Uniform Networking Configuration on a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Remove Hosts from a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Managing Networking on Host Proxy Switches
- Distributed Port Groups
- Working with Distributed Ports
- Configuring Virtual Machine Networking on a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Topology Diagrams of a vSphere Distributed Switch in the vSphere Web Client
- Setting Up VMkernel Networking
- VMkernel Networking Layer
- View Information About VMkernel Adapters on a Host
- Create a VMkernel Adapter on a vSphere Standard Switch
- Create a VMkernel Adapter on a Host Associated with a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Edit a VMkernel Adapter Configuration
- Overriding the Default Gateway of a VMkernel Adapter
- Configure the VMkernel Adapter Gateway by Using ESXCLI
- View TCP/IP Stack Configuration on a Host
- Change the Configuration of a TCP/IP Stack on a Host
- Create a Custom TCP/IP Stack
- Remove a VMkernel Adapter
- LACP Support on a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Convert to the Enhanced LACP Support on a vSphere Distributed Switch
- LACP Teaming and Failover Configuration for Distributed Port Groups
- Configure a Link Aggregation Group to Handle the Traffic for Distributed Port Groups
- Edit a Link Aggregation Group
- Enable LACP 5.1 Support on an Uplink Port Group
- Limitations of the LACP Support on a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Backing Up and Restoring Networking Configurations
- Rollback and Recovery of the Management Network
- Networking Policies
- Applying Networking Policies on a vSphere Standard or Distributed Switch
- Configure Overriding Networking Policies on Port Level
- Teaming and Failover Policy
- VLAN Policy
- Security Policy
- Traffic Shaping Policy
- Resource Allocation Policy
- Monitoring Policy
- Traffic Filtering and Marking Policy
- Traffic Filtering and Marking on a Distributed Port Group or Uplink Port Group
- Enable Traffic Filtering and Marking on a Distributed Port Group or Uplink Port Group
- Mark Traffic on a Distributed Port Group or Uplink Port Group
- Filter Traffic on a Distributed Port Group or Uplink Port Group
- Working with Network Traffic Rules on a Distributed Port Group or Uplink Port Group
- Disable Traffic Filtering and Marking on a Distributed Port Group or Uplink Port Group
- Traffic Filtering and Marking on a Distributed Port or Uplink Port
- Enable Traffic Filtering and Marking on a Distributed Port or Uplink Port
- Mark Traffic on a Distributed Port or Uplink Port
- Filter Traffic on a Distributed Port or Uplink Port
- Working with Network Traffic Rules on a Distributed Port or Uplink Port
- Disable Traffic Filtering and Marking on a Distributed Port or Uplink Port
- Qualifying Traffic for Filtering and Marking
- Traffic Filtering and Marking on a Distributed Port Group or Uplink Port Group
- Manage Policies for Multiple Port Groups on a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Port Blocking Policies
- Isolating Network Traffic by Using VLANs
- Managing Network Resources
- DirectPath I/O
- Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV)
- SR-IOV Support
- SR-IOV Component Architecture and Interaction
- vSphere and Virtual Function Interaction
- DirectPath I/O vs SR-IOV
- Configure a Virtual Machine to Use SR-IOV
- Networking Options for the Traffic Related to an SR-IOV Enabled Virtual Machine
- Using an SR-IOV Physical Adapter to Handle Virtual Machine Traffic
- Enabling SR-IOV by Using Host Profiles or an ESXCLI Command
- Virtual Machine That Uses an SR-IOV Virtual Function Fails to Power On Because the Host Is Out of Interrupt Vectors
- Remote Direct Memory Access for Virtual Machines
- Jumbo Frames
- TCP Segmentation Offload
- Enable or Disable Software TSO in the VMkernel
- Determine Whether TSO Is Supported on the Physical Network Adapters on an ESXi Host
- Enable or Disable TSO on an ESXi Host
- Determine Whether TSO Is Enabled on an ESXi Host
- Enable or Disable TSO on a Linux Virtual Machine
- Enable or Disable TSO on a Windows Virtual Machine
- Large Receive Offload
- Enable Hardware LRO for All VMXNET3 Adapters on an ESXi Host
- Enable or Disable Software LRO for All VMXNET3 Adapters on an ESXi Host
- Determine Whether LRO Is Enabled for VMXNET3 Adapters on an ESXi Host
- Change the Size of the LRO Buffer for VMXNET 3 Adapters
- Enable or Disable LRO for All VMkernel Adapters on an ESXi Host
- Change the Size of the LRO Buffer for VMkernel Adapters
- Enable or Disable LRO on a VMXNET3 Adapter on a Linux Virtual Machine
- Enable or Disable LRO on a VMXNET3 Adapter on a Windows Virtual Machine
- Enable LRO Globally on a Windows Virtual Machine
- NetQueue and Networking Performance
- vSphere Network I/O Control
- About vSphere Network I/O Control Version 3
- Upgrade Network I/O Control to Version 3 on a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Enable Network I/O Control on a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Bandwidth Allocation for System Traffic
- Bandwidth Allocation for Virtual Machine Traffic
- About Allocating Bandwidth for Virtual Machines
- Bandwidth Allocation Parameters for Virtual Machine Traffic
- Admission Control for Virtual Machine Bandwidth
- Create a Network Resource Pool
- Add a Distributed Port Group to a Network Resource Pool
- Configure Bandwidth Allocation for a Virtual Machine
- Configure Bandwidth Allocation on Multiple Virtual Machines
- Change the Quota of a Network Resource Pool
- Remove a Distributed Port Group from a Network Resource Pool
- Delete a Network Resource Pool
- Move a Physical Adapter Out the Scope of Network I/O Control
- Working with Network I/O Control Version 2
- MAC Address Management
- Configuring vSphere for IPv6
- Monitoring Network Connection and Traffic
- Capturing and Tracing Network Packets by Using the pktcap-uw Utility
- pktcap-uw Command Syntax for Capturing Packets
- pktcap-uw Command Syntax for Tracing Packets
- pktcap-uw Options for Output Control
- pktcap-uw Options for Filtering Packets
- Capturing Packets by Using the pktcap-uw Utility
- Trace Packets by Using the pktcap-uw Utility
- Configure the NetFlow Settings of a vSphere Distributed Switch
- Working With Port Mirroring
- vSphere Distributed Switch Health Check
- Switch Discovery Protocol
- Capturing and Tracing Network Packets by Using the pktcap-uw Utility
- Configuring Protocol Profiles for Virtual Machine Networking
- Multicast Filtering
- Stateless Network Deployment
- Networking Best Practices
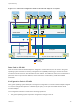
2 The VF forwards the request to the PF through a mailbox mechanism.
3 The PF driver checks the configuration request with the virtual switch (standard switch or host proxy
switch of a distributed switch).
4 The virtual switch verifies the configuration request against the policy on the port with which the VF
enabled virtual machine adapter is associated.
5 The PF driver configures the VF if the new settings are in compliance with the port policy of the virtual
machine adapter.
For example, if the VF driver tries to modify the MAC address, the address remains the same if MAC
address change is not allowed in the security policy for the port group or port. The guest operating
system might show that the change is successful but a log message indicates that the operation has
failed. As a result, the guest operating system and the virtual device save different MAC addresses.
The network interface in the guest operating system might not be able to acquire an IP address and
communicate. In this case, you have to reset the interface in the guest operating system to get the
latest MAC address from the virtual device and acquire an IP address.
vSphere and Virtual Function Interaction
Virtual functions (VFs) are lightweight PCIe functions that contain all the resources necessary for data
exchange but have a minimized set of configuration resources. Interaction between vSphere and VFs is
limited.
n
The physical NIC must use MSI-X interrupts.
n
VFs do not implement rate control in vSphere. Every VF can potentially use the entire bandwidth of a
physical link.
n
When a VF device is configured as a passthrough device on a virtual machine, the standby and
hibernate functions for the virtual machine are not supported.
n
The maximum number of VFs that you can create and the maximum number of VFs that you can use
for passthrough are different. The maximum number of VFs that you can instantiate depends on the
NIC capability and on the hardware configuration of the host. However, due to the limited number of
interrupt vectors available for passthrough devices, only a limited number of all instantiated VFs can
be used on an ESXi host.
The total number of interrupt vectors on each ESXi host can scale up to 4096 in the case of 32 CPUs.
When the host boots, devices on the host such as storage controllers, physical network adapters, and
USB controllers consume a subset of the 4096 vectors. If these devices require more than 1024
vectors, the maximum number of potentially supported VFs is reduced.
n
The number of VFs that is supported on an Intel NIC might be different from the number that is
supported on an Emulex NIC. See the technical documentation from the NIC vendor.
vSphere Networking
VMware, Inc. 156