7.3
Table Of Contents
- Life Cycle Extensibility
- Contents
- Life Cycle Extensibility
- Machine Extensibility Overview
- Extending Machine Lifecycles By Using vRealize Orchestrator
- Configuring Workflow Subscriptions to Extend vRealize Automation
- Event Topics Provided With vRealize Automation
- Workflow Subscriptions and Event Broker Terminology
- Blockable and Replyable Event Topics
- Best Practices for Creating vRealize Orchestrator Workflows for Workflow Subscriptions
- Workflow Subscription Settings
- Working with Provisioning and Life Cycle Workflow Subscriptions
- Configuring vRealize Orchestrator Workflows for Provisioning and Life Cycle Workflows
- Workflow Subscription Life Cycle State Definitions
- Configuring the Timeout Values for States and Events
- Configuring the Error Behavior for States and Events
- Scenario: Take a Post-Provisioning Snapshot of a Virtual Machine
- Working with Approval Workflow Subscriptions
- Troubleshooting Workflow Subscriptions
- Troubleshooting vRealize Orchestrator Workflows That Do Not Start
- Troubleshooting Provisioning Requests That Take Too Much Time
- Troubleshooting a vRealize Orchestrator Workflow That Does Not Run for an Approval Request
- Troubleshooting a Rejected Approval Request That Should Be Approved
- Troubleshooting a Rejected Approval Request
- Extending Machine Life Cycles By Using vRealize Automation Designer
- Extending Machine Life Cycles By Using vRealize Automation Designer Checklist
- Installing and Configuring vRealize Automation Designer
- Customizing IaaS Workflows By Using vRealize Automation Designer
- Workflows and Distributed Execution Management
- CloudUtil Command Reference
- vRealize Automation Workflow Activity Reference
- Index
The customizable workow templates provided by VMware demonstrate best practices for structuring
workows with separate sequences for initialization, custom logic, and nalization. The entire workow is
wrapped in a TryCatch block for error handling. Any uncaught or rethrown exceptions are logged by the
Distributed Execution Manager that executes the workow.
After you create a custom IaaS workow, a blueprint author must enable the workow on specic
blueprints.
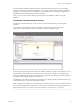
The vRealize Automation Designer Console
The vRealize Automation Designer console provides a visual workow editor for customizing IaaS
workows.
You must have local administrator rights on the vRealize Automation Designer host (typically a
development machine) in order to launch the vRealize Automation Designer console.
The Toolbox pane on the left provides access to the vRealize Automation workow activity library. You can
drag activities from the toolbox onto the Designer pane to add them to a workow. The Properties pane
displays the congurable properties of the currently selected activity on the Designer pane. This interface is
very similar to the workow designer in Visual Studio.
The detail tabs at the boom of the Designer pane enable you to display and edit variables within the scope
of the selected activity or arguments to the selected activity.
N Variables and arguments are both specied as Visual Basic expressions. However, variable names are
not case sensitive while argument names are case sensitive. For information about valid arguments for the
IaaS workow activities, see “vRealize Automation Workow Activity Reference,” on page 74.
Chapter 1 Life Cycle Extensibility
VMware, Inc. 49