Specifications
Table Of Contents
- Reference Guide
- Contents
- About This Book
- Getting Started
- Installation
- vCenter Server Heartbeat Implementation
- vCenter Server Heartbeat Installation on Windows Server 2003
- vCenter Server Heartbeat Installation on Windows Server 2008
- Configuring vCenter Server Heartbeat
- Server Configuration Wizard
- Configuring the Machine Identity
- Configuring the Server Role
- Configuring the Client Connection Port
- Configuring Channel IP Routing
- Configuring the Default Channel Port
- Configuring Low Bandwidth Module
- Configuring Public IP Addressing
- Enabling Network Monitoring
- Configuring Split-Brain Avoidance
- Managing vCenter Server Heartbeat License Keys
- Configuring Message Queue Logs
- Configuring the Maximum Disk Usage
- System Administration and Management
- Server Protection
- Network Protection
- Application Protection
- Status and Control
- Performance Protection
- Data Protection
- Data Protection Overview
- Other Administrative Tasks
- Troubleshooting
- Troubleshooting Unexpected Behaviors
- Two Active Servers
- Two Passive Servers
- Synchronization Failures
- Registry Status is Out of Sync
- Channel Drops
- Subnet or Routing Issues
- MaxDiskUsage Errors
- MaxDiskUsage Error Messages
- [L9]Exceeded the Maximum Disk Usage (VCChannelExceededMaxDiskUsageException)
- [L9]Exceeded the Maximum Disk Usage on the ACTIVE Server
- [L9]Exceeded the Maximum Disk Usage on the PASSIVE Server
- [L20]Out of Disk Space (VCChannelOutOfDiskSpaceException)
- Application Slowdown
- Poor Application Performance
- Both Servers Can Accommodate the Initial Load but the Load Has Increased
- One Server Can Provide Adequate Resource Support, but the Other Cannot
- Scheduled Resource Intensive Tasks
- Appendix - Setup Error Messages
- Glossary
Reference Guide
142 VMware, Inc.
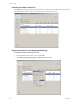
Adding a Service
To protect a service
1 Add the service from the vCenter Server Heartbeat Console in a Running state.
2Click Add to see a list of running services under Name.
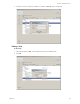
3 Select the service and set the values for Target State on Active and Target State on Passive. Normally the
Target State on Active is set to Running and the Target State on Passive is set to Stopped.
4 If vCenter Server Heartbeat is to manage the start and stop of the service, select Manage Starting and
Stopping. If vCenter Server Heartbeat is to monitor the state of the service, select Monitor State.
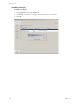
vCenter Server Heartbeat also assigns three sequential tasks to perform in the event of failure. Task
options include Recover Service, Application Restart, Log Warning, and any additional user-defined
tasks previously created.
5 Assign a task to each of the three failure options and click OK.
N
OTE Setting the target state for both the active and passive server to Running can cause the service to
place a lock on some files preventing synchronization from completing.
N
OTE For dependent services, failure actions must match the protected service.
N
OTE If an application with the failure option set to Application Restart fails, only the services that have
failed are restarted. Dependent services do not stop and restart as a result of the failure.