Installation Guide
Page
5
SunFrame
Unirac Code-Compliant Installation Manual
R
1411 Broadway Boulevard NE
Albuquerque NM 87102-1545 USA
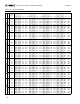
Step 4: Determine Net Design Wind Pressure, p
net30
(psf):
Using the Effective Wind Area (Step 2), Roof Zone Location
(Step 3), and Basic Wind Speed (Step 1), look up the
appropriate Net Design Wind Pressure in Table 2, page 6. Use
the Effective Wind Area value in the table which is smaller than
the value calculated in Step 2. If the installation is located on a
roof overhang, use Table 3, page 7.
Both downforce and uplift pressures must be considered
in overall design. Refer to Section II, Step 1 for applying
downforce and uplift pressures. Positive values are acting
toward the surface. Negative values are acting away from the
surface.
Figure 2. Enclosed buildings, wall and roofs
Flat Roof
Hip Roof (7˚ < θ ≤ 27°)
Gable Roof ( θ ≤ 7°) Gable Roof (7˚ < θ ≤ 45°)
Interior Zones
Roofs - Zone 1/Walls - Zone 4
End Zones
Roofs - Zone 2/Walls - Zone 5
Corner Zones
Roofs - Zone 3
Step 3: Determine Roof Zone (continued):
Using Roof Zone Setback Length, a, determine the roof zone
locations according to your roof type, gable, hip or monoslope.
Determine in which roof zone your pv system is located, Zone
1, 2, or 3 according to Figure 2.
Source: ASCE/SEI 7-05, Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other Structures, Chapter 6, p. 41.
h
a
a
a
a
h
a
a
a
a
a TYP
h
a
a
a
a
h
a
a
a
a