User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Part A – Preface
- Safety Information
- Revision History
- Important Information
- Compliance Information
- Part B – Feature Overview
- Introduction
- Features and Benefits
- Q Data Radio Range
- Part C – System Topologies & Operating Modes
- System Topologies
- Operating Modes
- Part D – Feature Detail
- Hardware
- Efficiency and Bandwidth
- Connectivity
- Ease of Use
- Security
- Part E – Radio Planning and Design
- Radio Path analysis
- BER & Fade Margin
- Radio Accessories
- RF Feeders and Protection
- Part F – Quick Reference Guide
- Introduction
- Half Duplex Radio - QR450
- Full Duplex Radio - QB450
- Hot Standby Half Duplex Radio - QP450
- Hot Standby Full Duplex Radio - QH450
- LED indicators
- Connecting Antennas
- Communication Ports
- Activating Transmitter
- Factory Default
- Digital I/O
- Connecting to Web User Interface (WUI)
- Resolving Ethernet Connection Issues
- Part G– Quick Start Guide
- Step-by-Step Point to Point Setup
- Step-by-Step eDiags Setup
- System Topology Configuration
- Serial and MODBUS
- Single Frequency (Simplex) Mode
- E-Series Emulation Mode
- Part H – Advanced
- Connectivity
- Ease of Use
- Security
- Part I – Installation & Commissioning
- Optimising the Antenna for Rx Signal
- Commissioning
- Part J – Firmware Updating and Maintenance
- Firmware Updating
- Global Firmware Updating
- Fuse Replacement - QR450
- Part K – Open Source License Acknowledgements
- Part L – Support Options
89
Document Number: 0100SM1401 Issue: 05-15
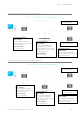
Serial and MODBUS
Serial data transport via TCP
Connect the PC’s Ethernet port to ETH1 or ETH2 of the radio being configured and using a web browser, browse to the
radio’s configuration page by entering the IP address the unit into the browser’s URL bar. Once the configuration has been
activated, repeat the process for the remaining radio.
To access the parameters below, browse to the “Setup” tab and select the “COM1” option under “Configuration”.
Remote - 192.168.2.17
COM1:
Mode: Serial Device Server
Character Layer and interface: match the
configuration of the external serial device you are
connecting to the Q data radios Serial Port. The
default is 9600,8,N,1 - RS232.
Packet Layer: MODBUS
Protocol: TCP
Protocol Mode: TCP Client
Primary IP Address: 192.168.2.16
Primary IP Port: 30010
Entry Point - 192.168.2.16
COM1:
Mode: Serial Device Server
Character Layer and Interface: match the
configuration of the external serial device you
are connecting to the Q data radio’s Serial Port.
The default is 9600,8,N,1 - RS232.
Packet Layer: MODBUS
Protocol: TCP
Protocol Mode: TCP Server
Local IP Port: 30010
Inactivity Timeout: 30 seconds.
Serial data transport via UDP
Connect the PC’s Ethernet port to ETH1 or ETH2 of the radio being configured and using a web browser, browse to the
radio’s configuration page by entering the IP address the unit into the browser’s URL bar. Once the configuration has been
activated, repeat the process for the remaining radio.
To access the parameters below, browse to the “Setup” tab and select the “COM1” option under “Configuration”.
Remote - 192.168.2.17
COM1:
Mode: Serial Device Server
Character Layer and interface: match the
configuration of the external serial device you are
connecting to the Q data radios Serial Port. The
default is 9600,8,N,1 - RS232.
Packet Layer: MODBUS
Protocol: UDP
Protocol Mode: Point to point
UDP listen mode: static
Remote IP Address: 192.168.2.16
Remote IP Port: 30010
Local IP Port: 30010
Entry Point - 192.168.2.16
COM1:
Mode: Serial Device Server
Character Layer and Interface: match the
configuration of the external serial device you
are connecting to the Q data radio’s Serial Port.
The default is 9600,8,N,1 - RS232.
Packet Layer: MODBUS
Protocol: UDP
Protocol Mode: Point to point
UDP listen mode: static
Remote IP Address: 192.168.2.17
Remote IP Port: 30010
Local IP Port: 30010
Introduction
Point to Point serial connectivity can be achieved by using the serial device server embedded within the Q data radios radio. The serial
device server has three protocols available, each with their own benefits:
TCP: Establishes a session based connection, providing high reliability on data delivery.
UDP: Consumes low bandwidth and provides a low latency connection.
PPP: Provides a virtual Ethernet connection over a serial link.
Part G – Quick Start Guide