User Manual
Table Of Contents
- 1 Features
- 2 First Steps with TMCL
- 3 TMCL and the TMCL-IDE — An Introduction
- 3.1 Binary Command Format
- 3.2 Reply Format
- 3.3 Standalone Applications
- 3.4 TMCL Command Overview
- 3.5 TMCL Commands by Subject
- 3.6 Detailed TMCL Command Descriptions
- 3.6.1 ROR (Rotate Right)
- 3.6.2 ROL (Rotate Left)
- 3.6.3 MST (Motor Stop)
- 3.6.4 MVP (Move to Position)
- 3.6.5 SAP (Set Axis Parameter)
- 3.6.6 GAP (Get Axis Parameter)
- 3.6.7 SGP (Set Global Parameter)
- 3.6.8 GGP (Get Global Parameter)
- 3.6.9 STGP (Store Global Parameter)
- 3.6.10 RSGP (Restore Global Parameter)
- 3.6.11 RFS (Reference Search)
- 3.6.12 SIO (Set Output)
- 3.6.13 GIO (Get Input)
- 3.6.14 CALC (Calculate)
- 3.6.15 COMP (Compare)
- 3.6.16 JC (Jump conditional)
- 3.6.17 JA (Jump always)
- 3.6.18 CSUB (Call Subroutine)
- 3.6.19 RSUB (Return from Subroutine)
- 3.6.20 WAIT (Wait for an Event to occur)
- 3.6.21 STOP (Stop TMCL Program Execution – End of TMCL Program)
- 3.6.22 SCO (Set Coordinate)
- 3.6.23 GCO (Get Coordinate)
- 3.6.24 CCO (Capture Coordinate)
- 3.6.25 ACO (Accu to Coordinate)
- 3.6.26 CALCX (Calculate using the X Register)
- 3.6.27 AAP (Accu to Axis Parameter)
- 3.6.28 AGP (Accu to Global Parameter)
- 3.6.29 CLE (Clear Error Flags)
- 3.6.30 EI (Enable Interrupt)
- 3.6.31 DI (Disable Interrupt)
- 3.6.32 VECT (Define Interrupt Vector)
- 3.6.33 RETI (Return from Interrupt)
- 3.6.34 Customer specific Command Extensions (UF0…UF7 – User Functions)
- 3.6.35 Request Target Position reached Event
- 3.6.36 TMCL Control Commands
- 4 Axis Parameters
- 5 Global Parameters
- 6 Hints and Tips
- 7 TMCL Programming Techniques and Structure
- 8 Figures Index
- 9 Tables Index
- 10 Supplemental Directives
- 11 Revision History
TMCM-3212 TMCL
™
Firmware Manual • Firmware Version V1.07 | Document Revision V1.04 • 2017-JUN-08
97 / 103
7.5 Using Subroutines
The CSUB and RSUB commands provide a mechanism for using subroutines. The CSUB command branches
to the given label. When an RSUB command is executed the control goes back to the command that
follows the CSUB command that called the subroutine.
This mechanism can also be nested. From a subroutine called by a CSUB command other subroutines can
be called. In the current version of TMCL eight levels of nested subroutine calls are allowed.
7.6 Combining Direct Mode and Standalone Mode
Direct mode and standalone mode can also be combined. When a TMCL program is being executed in
standalone mode, direct mode commands are also processed (and they do not disturb the flow of the
program running in standalone mode). So, it is also possible to query e.g. the actual position of the motor
in direct mode while a TMCL program is running.
Communication between a program running in standalone mode and a host can be done using the TMCL
user variables. The host can then change the value of a user variable (using a direct mode SGP command)
which is regularly polled by the TMCL program (e.g. in its main loop) and so the TMCL program can react
on such changes. Vice versa, a TMCL program can change a user variable that is polled by the host (using a
direct mode GGP command).
A TMCL program can be started by the host using the run command in direct mode. This way, also a set
of TMCL routines can be defined that are called by a host. In this case it is recommended to place JA
commands at the beginning of the TMCL program that jump to the specific routines. This assures that
the entry addresses of the routines will not change even when the TMCL routines are changed (so when
changing the TMCL routines the host program does not have to be changed).
Example:
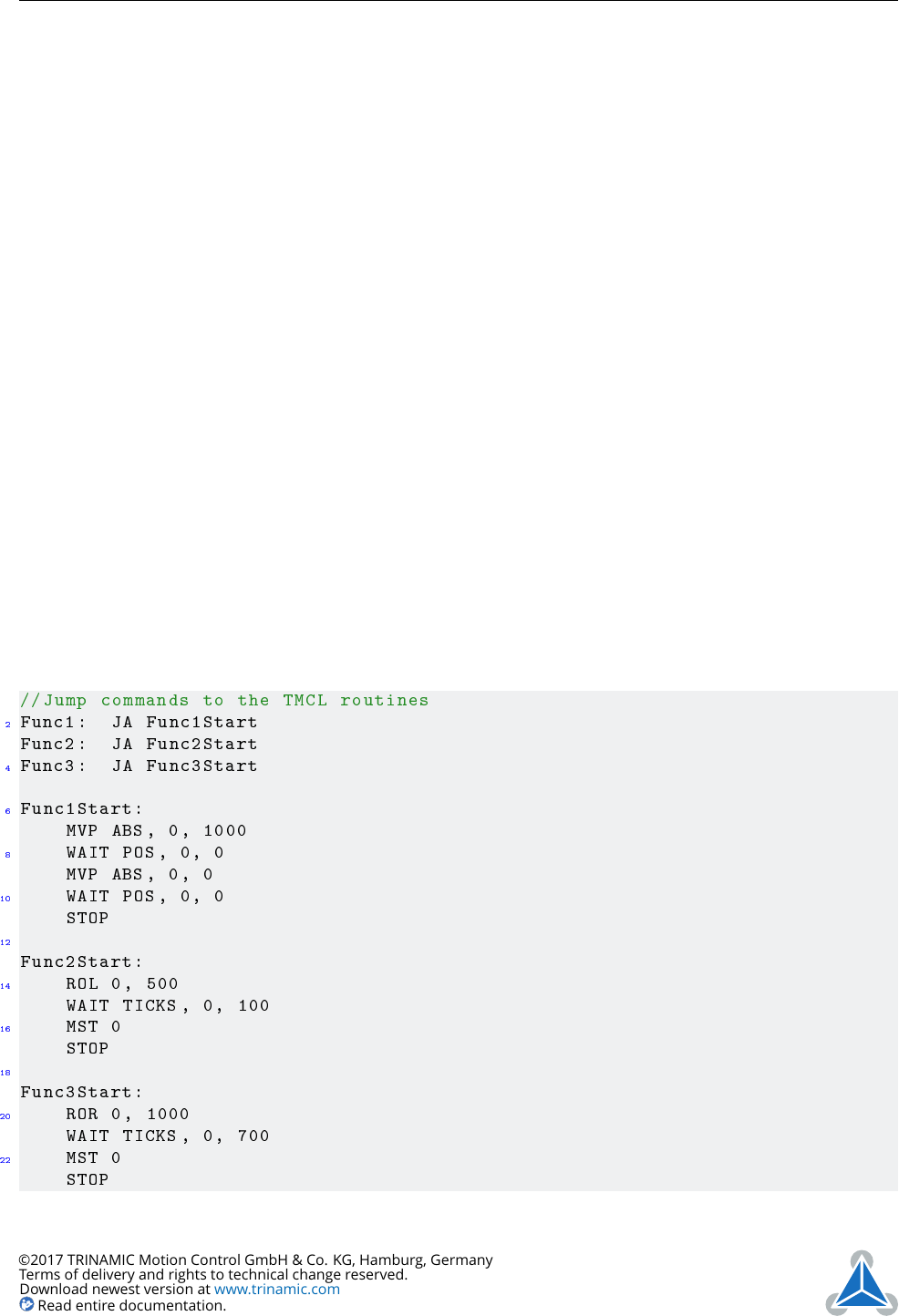
//Jump commands to the TMCL routines
2
Func1: JA Func1Start
Func2: JA Func2Start
4
Func3: JA Func3Start
6
Func1Start:
MVP ABS , 0, 1000
8
WAIT POS , 0, 0
MVP ABS , 0, 0
10
WAIT POS , 0, 0
STOP
12
Func2Start:
14
ROL 0, 500
WAIT TICKS , 0, 100
16
MST 0
STOP
18
Func3Start:
20
ROR 0, 1000
WAIT TICKS , 0, 700
22
MST 0
STOP
©2017 TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG, Hamburg, Germany
Terms of delivery and rights to technical change reserved.
Download newest version at www.trinamic.com
Read entire documentation.










