User Manual
Basic Configuration via Browser Interface
Trango Broadband Wireless — User Manual Access5830 Rev. D
Page 9
Section 4 Basic Configuration via Browser Interface
This section describes a few more basic concepts and how to establish a basic wireless link between AP and SU, using the Browser
(HTTP) Interface . This section is written to address only the most basic steps in establishing a link in the lab, or a bench-top
environment. It is highly recommended to read the other sections of this manual to gain an understanding of all important
configuration parameters and procedures prior to deploying any wireless equipment.
In this section you will:
?? Learn about AP and SU Basic Configuration Screens and Parameters
?? Populate Access Point’s Subscriber Unit Data Bases (SUDB) with at least one SU.
?? Configure Other Basic AP Parameters
?? Configure Basic SU Parameters
?? Establish a Wireless Link
?? Evaluate Link Quality
The Access5830 uses the concept of “association” to indicate that the APs and SUs are communicating. If all parameters are properly
set, the AP will begin actively searching for the SUs in its SU database (SUDB). Once an active SU is detected, the authentication and
association process will begin.
Essentials to Establish a Wireless Link with M900S Series Radios
?? Base ID in AP and SU must match
?? MAC Address of SU must match an entry in the subscriber unit database (SUDB)
?? AP must be in Opmode “AP”
?? SU must be in Opmode “SU”
?? Adequate signal strength must be received at each radio
If all of these parameters are met, and if the AP and SU are within range - and properly aligned, the wireless link will automatically
establish itself and Ethernet traffic will begin to pass between the radios.
? Note: This section utilizes the Browser Interface as the configuration tool. For the equivalent CLI commands, see Section 5.
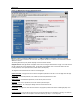
Configuring AP Subscriber Unit Database
Prior to establishing a wireless link, the user must configure the Subscriber Unit Database (SUDB) in the AP with each SU’s MAC
address and related settings. The subscriber unit database includes detailed information about each SU. The user uses the
Subscriber Database page to add, modify, and delete SUs. The key information for each SU includes the following:
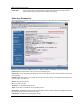
SU ID: User Definable subscriber unit ID (1…8190)
TYPE: PR Priority or REG Regular. Priority SUs are favored in the dynamic polling process and thus respond with
less latency than regular SUs.
Group: SU to SU Group # (1..F in hex) for SU to SU communications. Only SUs with same SU to SU group # may
communicate with each another.
CIR UP: Committed Information Rate from SU to AP. Minimum upstream rate (measured in Kbps) at which the SU will
attempt to deliver bandwidth to the AP. Maximum setting is 3000.
CIR DOWN: Committed Information Rate from AP to SU. Minimum rate (measured in Kbps) at which the AP will attempt to
deliver bandwidth to this SU. Maximum setting is 3000.
MIR UP: Maximum Information Rate from SU to AP. Maximum upstream rate (measured in Kbps) at which the SU will
attempt to deliver bandwidth to the AP. Maximum setting is 3000.
MIR UP: Maximum Information Rate from AP to SU. Maximum rate (measured in Kbps) at which the AP will attempt to
deliver bandwidth to this SU. Maximum setting is 3000.
DEVICE ID: MAC address of the SU. The MAC address and BASE ID are the basis for authentication with the AP.