User Guide
Table Of Contents
- Package Contents
- Chapter 1 About this Guide
- Chapter 2 Introduction
- Chapter 3 Login to the Switch
- Chapter 4 System
- Chapter 5 Switching
- Chapter 6 VLAN
- Chapter 7 Spanning Tree
- Chapter 8 Multicast
- Chapter 9 QoS
- Chapter 10 ACL
- Chapter 11 Network Security
- Chapter 12 SNMP
- Chapter 13 LLDP
- Chapter 14 Cluster
- Chapter 15 Maintenance
- Chapter 16 System Maintenance via FTP
- Appendix A: Specifications
- Appendix B: Configuring the PCs
- Appendix C: 802.1X Client Software
- Appendix D: Glossary
With BPDU filter function
enabled, a port does not receive or forward BPDUs, but it sends out its
own BPDUs. Such a mechanism prevents the switch from being attacked by BPDUs so as to
guarantee generation the spanning trees correct.
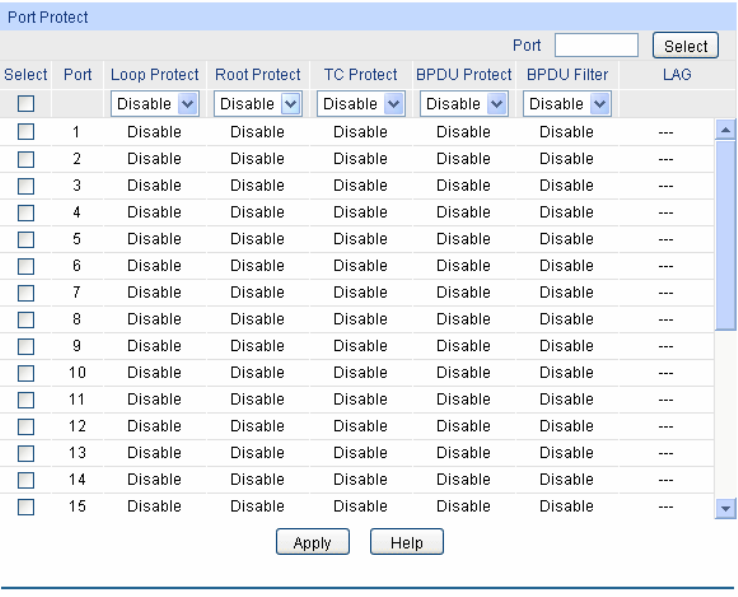
Choose the menu Spanning Tree→STP Security→Port Protect to load the following page.
Figure 7-10 Port Protect
The following entries are displayed on this screen:
Port Protect
Port Select: Click the Select button to quick-select the corresponding port based
on the port number you entered.
Select: Select the desired port for port protect configuration. It is
multi-optional.
Port: Displays the port number of the switch.
Loop Protect: Loop Protect is to prevent the loops in the network brought by
recalculating STP because of link failures and network congestions.
Root Protect: Root Protect is to prevent wrong network topology change caused by
the role change of the current legal root bridge.
TC Protect: TC Protect is to prevent the decrease of the performance and stability
of the switch brought by continuously removing MAC address entries
upon receiving TC-BPDUs in the STP network.
BPDU Protect: BPDU Protect is to prevent the edge port from being attacked by
maliciously created BPDUs
BPDU Filter: BPDU Filter is to prevent BPDUs flood in the STP network.
LAG: Displays the LAG number which the port belongs to.
93










