Computer Hardware User's Guide
Clocking Memory Accesses
8-30
If
dst1
and
dst2
are both written to external memory, a single CPU cycle
is still all that is necessary to complete the stores. In this case, four bus
cycles are required.
1) In the first cycle, both
dst1
and
dst2
are written to the port, and the ex-
ternal-bus access for
dst1
begins.
a) The store for
dst1
is completed on the second cycle.
b) The store for
dst2
begins on the third external-bus cycle.
c) The store for
dst2
is completed on the fourth external-bus cycle.
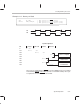
8.5.2.4 Parallel Multiplies and Adds
Memory addressing for parallel multiplies and adds is similar to that for 3-operand
instructions. The parallel multiplies and adds include all instructions with bits
31–30 = 10 (see Figure 8–7).
Figure 8–7. Parallel Multiplies and Adds
31
10
P
src
4
24 23 16 15 8 7 0
src
1
src
3
Operation d1
d2
src
2
For these operations,
src3
and
src4
are both located in memory. If both operands
are located in internal memory,
src3
is performed during H3, and
src4
is per-
formed during H1, thus completing two memory reads in a single cycle.
If
src3
is in internal memory and
src4
is in external memory, the
src4
access
begins at the start of H3 and latches at the end of H1. At the same time, the
src3
access to internal memory is performed during H3. Again, two memory
reads are completed in a single cycle.
If
src3
is in external memory and
src4
is in internal memory, two cycles
are necessary to complete the two reads. In the first cycle, the internal
src4
access is performed. During the H3 of the next cycle, the
src3
access is
performed.
If
src3
and
src4
are both from external memory, two cycles are necessary
to complete the two reads. In the first cycle, the
src3
access is performed;
in the second cycle, the
src4
access is performed.