Datasheet
Table Of Contents
- FEATURES
- APPLICATIONS
- DESCRIPTION
- TYPICAL APPLICATION
- ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
- THERMAL INFORMATION
- ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
- PIN CONFIGURATION
- TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
- APPLICATION INFORMATION
- GENERAL DESCRIPTION
- COMMUNICATION PROTOCOL
- COMMAND REGISTER
- GLOBAL INITIALIZATION AND ADDRESS ASSIGNMENT SEQUENCE
- GLOBAL READ AND WRITE
- GLOBAL CLEAR INTERRUPT
- GLOBAL SOFTWARE RESET
- INDIVIDUAL READ AND WRITE
- TEMPERATURE REGISTER
- CONFIGURATION REGISTER
- TEMPERATURE LIMIT REGISTERS
- TIMEOUT FUNCTION
- NOISE
- SMAART WIRE INTERFACE TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
- Revision History
TMP104
www.ti.com
SBOS564A –NOVEMBER 2011– REVISED NOVEMBER 2011
Negative numbers are represented in binary twos complement format. Following power-up or reset, the
Temperature Register reads 0°C until the first conversion is complete.
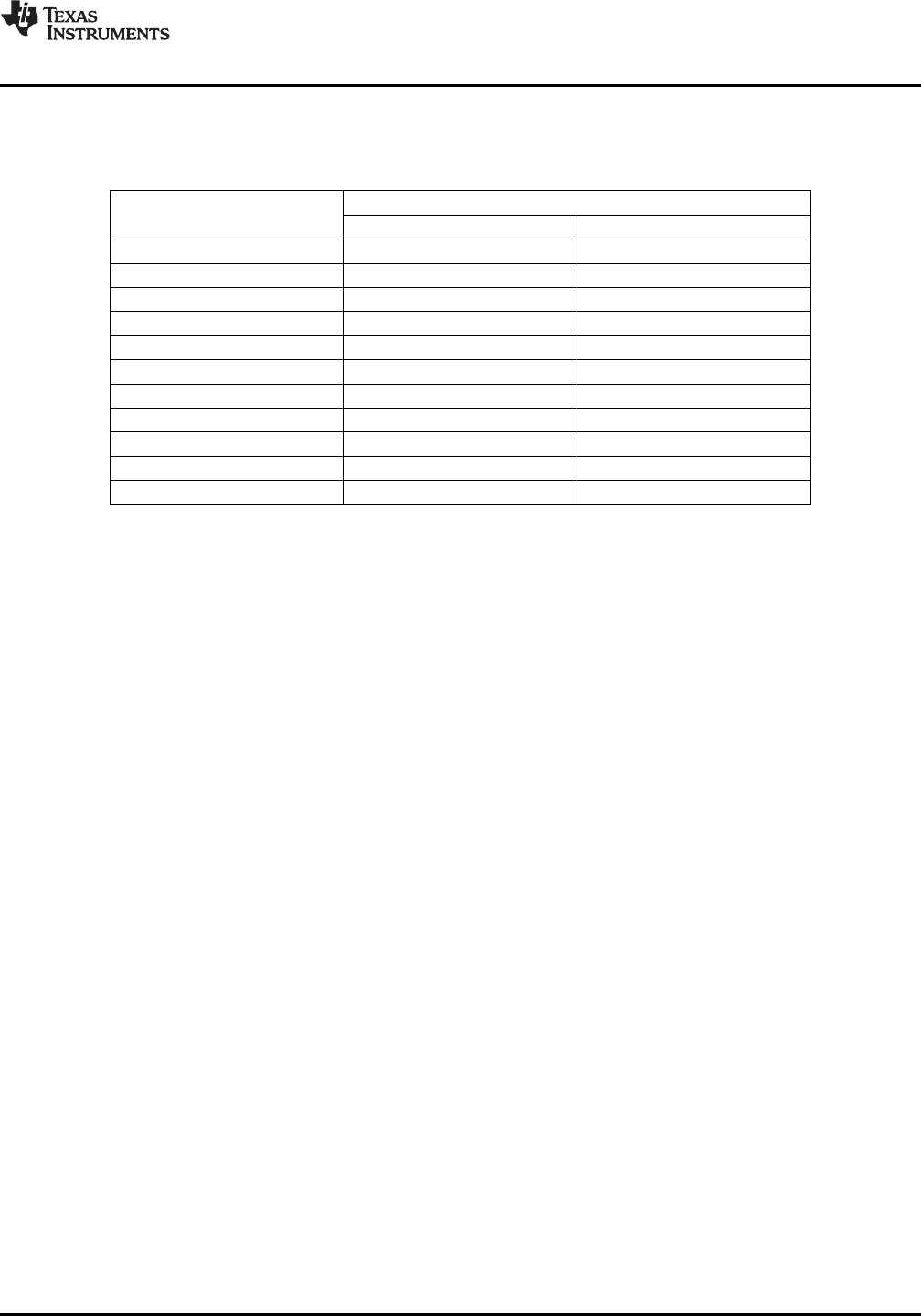
Table 5. 8-Bit Temperature Data Format
(1)
DIGITAL OUTPUT
TEMPERATURE (°C) BINARY HEX
128 0111 1111 7F
127 0111 1111 7F
100 0110 0100 64
80 0101 0000 50
75 0100 1011 4B
50 0011 0010 32
25 0001 1001 19
0 0000 0000 00
–1 1111 1111 FF
–25 1110 0111 E7
–55 1100 1001 C9
(1) The resolution for the analog-to-digital converter (ADC) is 1°C/count, where count is equal to the digital
output of the ADC.
For positive temperatures (for example, +50°C):
Twos complement is not performed on positive numbers. Therefore, simply convert the number to binary
code, left-justified format. Denote a positive number with most significant bit (MSB) = 0.
Example: (+50°C)/(1°C/count) = 50 = 32h = 0011 0010
For negative temperatures (for example, –25°C):
Generate the twos complement of a negative number by complementing the absolute value binary number
and adding 1. Denote a negative number with MSB = 1.
Example: (|–25°C|)/(1°C/count) = 25 = 19h = 0001 1001
Twos complement format: 1110 0110 + 1 = 1110 0111
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 11
Product Folder Link(s): TMP104