Datasheet
Table Of Contents
- FEATURES
- APPLICATIONS
- DESCRIPTION
- PINOUT INFORMATION
- ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
- THERMAL INFORMATION
- RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
- ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
- TIMING REQUIREMENTS
- TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
- SYSTEM DIAGRAMS
- APPLICATION INFORMATION
- ECCENTRIC ROTATING MASS MOTORS (ERM)
- LINEAR RESONANCE ACTUATORS (LRA)
- AUTO-RESONANCE ENGINE FOR LRA
- OPEN LOOP OPERATION FOR LRA
- SMART LOOP ARCHITECTURE
- AUTO CALIBRATION
- WAVEFORM LIBRARIES
- WAVEFORM SEQUENCER
- LIBRARY PARAMETERIZATION
- REAL-TIME PLAYBACK (RTP) MODE
- MULTI-MODE INPUT PIN (IN/TRIG)
- DEVICE ENABLE
- CONSTANT VIBRATION STRENGTH
- EDGE RATE CONTROL
- CAPACITOR SELECTION
- MODES OF OPERATION
- BLOCK DIAGRAM
- GENERAL I2C OPERATION
- SINGLE-BYTE AND MULTIPLE-BYTE TRANSFERS
- SINGLE-BYTE WRITE
- MULTIPLE-BYTE WRITE AND INCREMENTAL MULTIPLE-BYTE WRITE
- SINGLE-BYTE READ
- MULTIPLE-BYTE READ
- REGISTER MAP
- DEVICE PROGRAMMING
- WAVEFORM LIBRARY EFFECTS LIST
- PCB LAYOUT RECOMMENDATIONS
- Revision History
A6 A0 ACK
Acknowledge
I CDevice Addressand
Read/WriteBit
2
R/WA6 A0 R/W ACK A0 ACK D7 D0 ACK
Start
Condition
Stop
Condition
Acknowledge Acknowledge Acknowledge
LastDataByte
ACK
FirstDataByte
RepeatStart
Condition
Not
Acknowledge
I CDevice Addressand
Read/WriteBit
2
Subaddress OtherDataBytes
A7 A6 A5 D7 D0 ACK
Acknowledge
D7 D0
T0484-01
A6 A5 A0 R/W ACK A7 A6 A5 A4 A0 ACK A6 A5 A0 ACK
Start
Condition
Stop
Condition
Acknowledge Acknowledge Acknowledge
I CDevice Addressand
Read/WriteBit
2
Subaddress DataByte
D7 D6 D1 D0 ACK
I CDevice Addressand
Read/WriteBit
2
Not
Acknowledge
R/WA1 A1
RepeatStart
Condition
T0483-01
DRV2605
SLOS825B –DECEMBER 2012–REVISED JANUARY 2014
www.ti.com
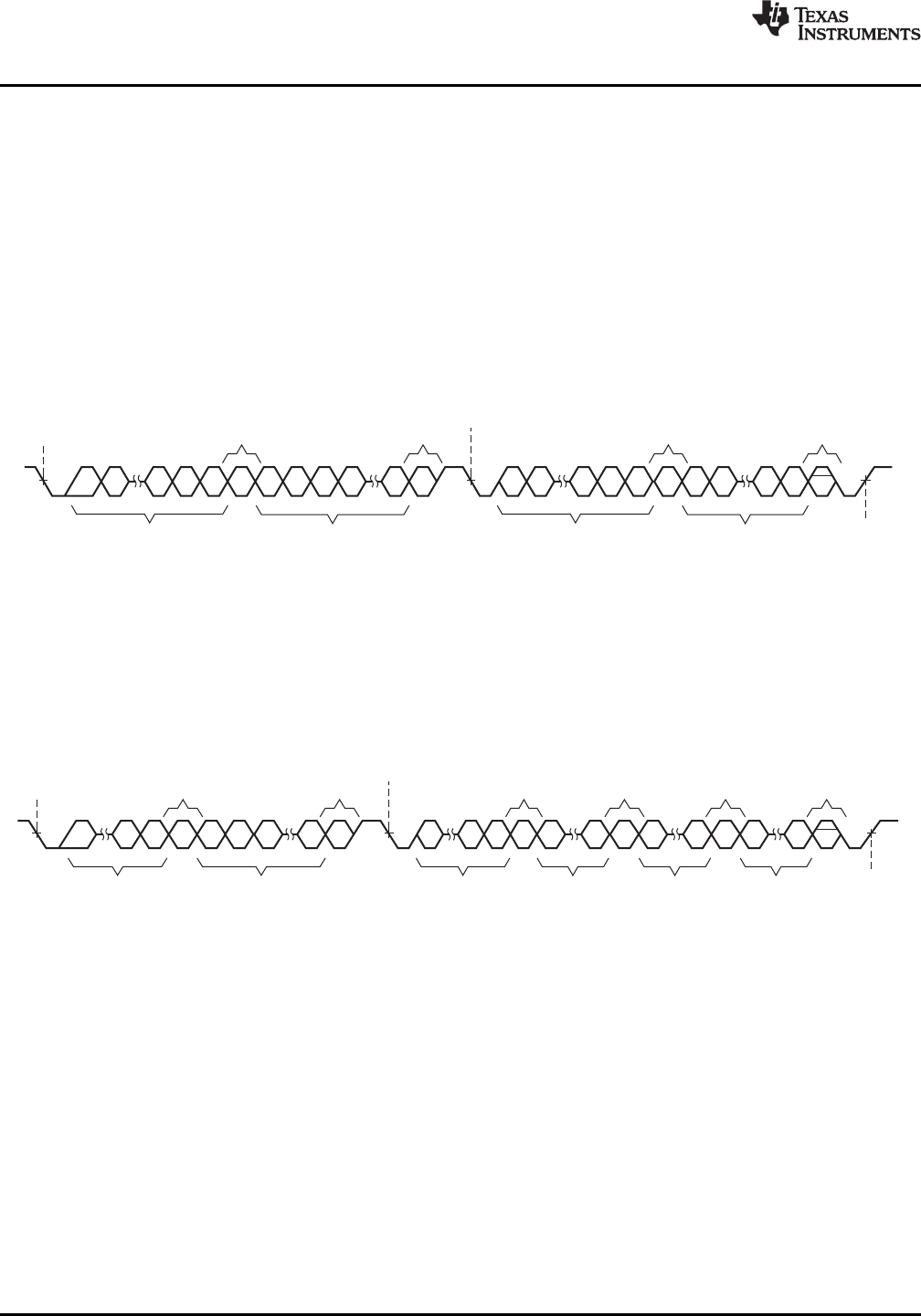
SINGLE-BYTE READ
As shown in Figure 22, a single-byte data-read transfer begins with the master device transmitting a start
condition followed by the I
2
C device address and the read/write bit. For the data-read transfer, both a write
followed by a read are actually done. Initially, a write is done to transfer the address byte of the internal memory
address to be read. As a result, the read/write bit is set to a 0.
After receiving the DRV2605 address and the read/write bit, the DRV2605 responds with an acknowledge bit.
The master then sends the internal memory address byte, after which the DRV2605 issues an acknowledge bit.
The master device transmits another start condition followed by the DRV2605 address and the read/write bit
again. This time, the read/write bit is set to 1, indicating a read transfer. Next, the DRV2605 transmits the data
byte from the memory address being read. After receiving the data byte, the master device transmits a not-
acknowledge followed by a stop condition to complete the single-byte data read transfer.
The DRV2605 address is 0x5A (7-bit), or 1011010 in binary.
Figure 22. Single-Byte Read Transfer
MULTIPLE-BYTE READ
A multiple-byte data-read transfer is identical to a single-byte data-read transfer except that multiple data bytes
are transmitted by the DRV2605 to the master device as shown in Figure 23. With the exception of the last data
byte, the master device responds with an acknowledge bit after receiving each data byte.
Figure 23. Multiple-Byte Read Transfer
22 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2012–2014, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: DRV2605










