User manual
Table Of Contents
- Read This First
- Contents
- Figures
- Tables
- Examples
- Cautions
- Introduction
- Architectural Overview
- Central Processing Unit
- Memory and I/O Spaces
- Program Control
- Addressing Modes
- Assembly Language Instructions
- Instruction Set Summary
- How To Use the Instruction Descriptions
- Instruction Descriptions
- ABS
- ABS
- ADD
- ADD
- ADD
- ADD
- ADDC
- ADDC
- ADDS
- ADDS
- ADDT
- ADDT
- ADRK
- AND
- AND
- AND
- APAC
- APAC
- B
- BACC
- BANZ
- BANZ
- BCND
- BCND
- BIT
- BIT
- BITT
- BITT
- BLDD
- BLDD
- BLDD
- BLDD
- BLDD
- BLPD
- BLPD
- BLPD
- BLPD
- CALA
- CALL
- CC
- CC
- CLRC
- CLRC
- CMPL
- CMPR
- DMOV
- DMOV
- IDLE
- IN
- IN
- INTR
- LACC
- LACC
- LACC
- LACL
- LACL
- LACL
- LACT
- LACT
- LAR
- LAR
- LAR
- LDP
- LDP
- LPH
- LPH
- LST
- LST
- LST
- LST
- LT
- LT
- LTA
- LTA
- LTD
- LTD
- LTD
- LTP
- LTP
- LTS
- LTS
- MAC
- MAC
- MAC
- MAC
- MACD
- MACD
- MACD
- MACD
- MACD
- MAR
- MAR
- MPY
- MPY
- MPY
- MPYA
- MPYA
- MPYS
- MPYS
- MPYU
- MPYU
- NEG
- NEG
- NMI
- NOP
- NORM
- NORM
- NORM
- OR
- OR
- OR
- OUT
- OUT
- PAC
- POP
- POP
- POPD
- POPD
- PSHD
- PSHD
- PUSH
- RET
- RETC
- ROL
- ROR
- RPT
- RPT
- SACH
- SACH
- SACL
- SACL
- SAR
- SAR
- SBRK
- SETC
- SETC
- SFL
- SFR
- SFR
- SPAC
- SPH
- SPH
- SPL
- SPL
- SPLK
- SPLK
- SPM
- SQRA
- SQRA
- SQRS
- SQRS
- SST
- SST
- SUB
- SUB
- SUB
- SUB
- SUBB
- SUBB
- SUBC
- SUBC
- SUBS
- SUBS
- SUBT
- SUBT
- TBLR
- TBLR
- TBLR
- TBLW
- TBLW
- TBLW
- TRAP
- XOR
- XOR
- XOR
- ZALR
- ZALR
- On-Chip Peripherals
- Synchronous Serial Port
- Asynchronous Serial Port
- TMS320C209
- Register Summary
- TMS320C1x/C2x/C2xx/C5x Instruction Set Comparison
- Program Examples
- Submitting ROM Codes to TI
- Design Considerations for Using XDS510 Emulator
- E.1 Designing Your Target System’s Emulator Connector (14-Pin Header)
- E.2 Bus Protocol
- E.3 Emulator Cable Pod
- E.4 Emulator Cable Pod Signal Timing
- E.5 Emulation Timing Calculations
- E.6 Connections Between the Emulator and the Target System
- E.7 Physical Dimensions for the 14-Pin Emulator Connector
- E.8 Emulation Design Considerations
- Glossary
- Index
Using the Instruction Set Comparison Table
B-2
B.1 Using the Instruction Set Comparison Table
To help you read the comparison table, this section provides an example of a
table entry and a list of acronyms.
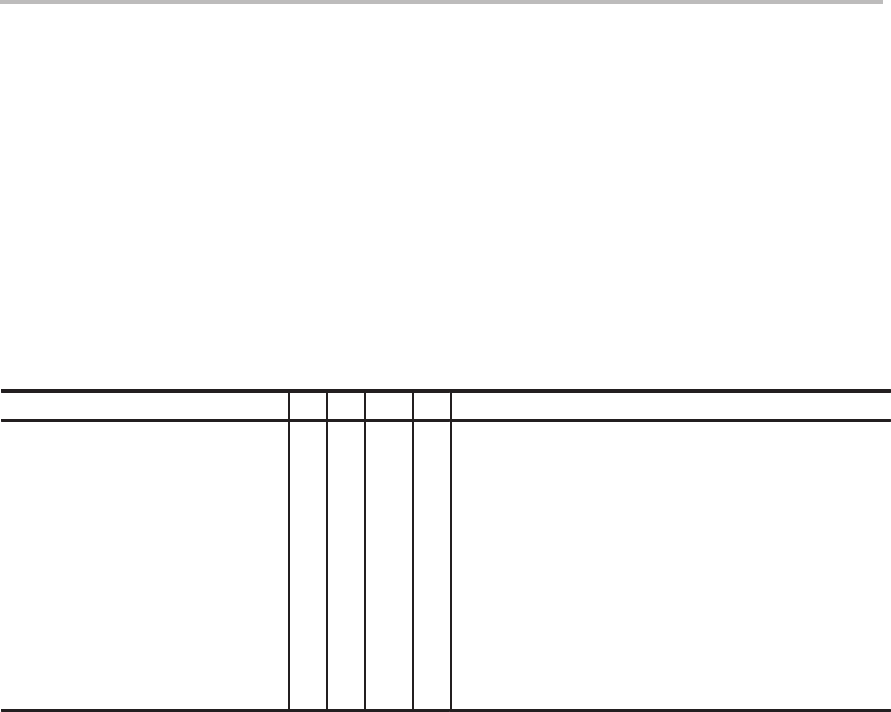
B.1.1 An Example of a Table Entry
In cases where more than one syntax is used, the first syntax is usually for di-
rect addressing and the second is usually for indirect addressing. Where three
or more syntaxes are used, the syntaxes are normally specific to a device.
This is how the AND instruction appears in the table:
Syntax
1x 2x 2xx 5x Description
AND
dma
AND {
ind
} [ ,
next ARP
]
AND #
lk
[ ,
shift
]
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
AND With Accumulator
TMS320C1x and TMS320C2x devices: AND the con-
tents of the addressed data-memory location with the
16 LSBs of the accumulator. The 16 MSBs of the accu-
mulator are ANDed with 0s.
TMS320C2xx and TMS320C5x devices: AND the con-
tents of the addressed data-memory location or a
16-bit immediate value with the contents of the accu-
mulator. The 16 MSBs of the accumulator are ANDed
with 0s. If a shift is specified, left shift the constant be-
fore the AND. Low-order bits below and high-order bits
above the shifted value are treated as 0s.
The first column,
Syntax
, states the mnemonic and the syntaxes for the AND
instruction.
The checks in the second through the fifth columns,
1x
,
2x
,
2xx,
and
5x
, indi-
cate the devices that can be used with each of the syntaxes.
1x refers to the TMS320C1x devices
2x refers to the TMS320C2x devices, including TMS320C25
2xx refers to the TMS320C2xx devices
5x refers to the TMS320C5x devices
In this example, you can use the first two syntaxes with TMS320C1x,
TMS320C2x, TMS320C2xx, and TMS320C5x devices, but you can use the
last syntax only with TMS320C2xx and TMS320C5x devices.
The sixth column,
Description
, briefly describes how the instruction functions.
Often, an instruction functions slightly differently for the different devices: read
the entire description before using the instruction.










