User manual
Table Of Contents
- Read This First
- Contents
- Figures
- Tables
- Examples
- Cautions
- Introduction
- Architectural Overview
- Central Processing Unit
- Memory and I/O Spaces
- Program Control
- Addressing Modes
- Assembly Language Instructions
- Instruction Set Summary
- How To Use the Instruction Descriptions
- Instruction Descriptions
- ABS
- ABS
- ADD
- ADD
- ADD
- ADD
- ADDC
- ADDC
- ADDS
- ADDS
- ADDT
- ADDT
- ADRK
- AND
- AND
- AND
- APAC
- APAC
- B
- BACC
- BANZ
- BANZ
- BCND
- BCND
- BIT
- BIT
- BITT
- BITT
- BLDD
- BLDD
- BLDD
- BLDD
- BLDD
- BLPD
- BLPD
- BLPD
- BLPD
- CALA
- CALL
- CC
- CC
- CLRC
- CLRC
- CMPL
- CMPR
- DMOV
- DMOV
- IDLE
- IN
- IN
- INTR
- LACC
- LACC
- LACC
- LACL
- LACL
- LACL
- LACT
- LACT
- LAR
- LAR
- LAR
- LDP
- LDP
- LPH
- LPH
- LST
- LST
- LST
- LST
- LT
- LT
- LTA
- LTA
- LTD
- LTD
- LTD
- LTP
- LTP
- LTS
- LTS
- MAC
- MAC
- MAC
- MAC
- MACD
- MACD
- MACD
- MACD
- MACD
- MAR
- MAR
- MPY
- MPY
- MPY
- MPYA
- MPYA
- MPYS
- MPYS
- MPYU
- MPYU
- NEG
- NEG
- NMI
- NOP
- NORM
- NORM
- NORM
- OR
- OR
- OR
- OUT
- OUT
- PAC
- POP
- POP
- POPD
- POPD
- PSHD
- PSHD
- PUSH
- RET
- RETC
- ROL
- ROR
- RPT
- RPT
- SACH
- SACH
- SACL
- SACL
- SAR
- SAR
- SBRK
- SETC
- SETC
- SFL
- SFR
- SFR
- SPAC
- SPH
- SPH
- SPL
- SPL
- SPLK
- SPLK
- SPM
- SQRA
- SQRA
- SQRS
- SQRS
- SST
- SST
- SUB
- SUB
- SUB
- SUB
- SUBB
- SUBB
- SUBC
- SUBC
- SUBS
- SUBS
- SUBT
- SUBT
- TBLR
- TBLR
- TBLR
- TBLW
- TBLW
- TBLW
- TRAP
- XOR
- XOR
- XOR
- ZALR
- ZALR
- On-Chip Peripherals
- Synchronous Serial Port
- Asynchronous Serial Port
- TMS320C209
- Register Summary
- TMS320C1x/C2x/C2xx/C5x Instruction Set Comparison
- Program Examples
- Submitting ROM Codes to TI
- Design Considerations for Using XDS510 Emulator
- E.1 Designing Your Target System’s Emulator Connector (14-Pin Header)
- E.2 Bus Protocol
- E.3 Emulator Cable Pod
- E.4 Emulator Cable Pod Signal Timing
- E.5 Emulation Timing Calculations
- E.6 Connections Between the Emulator and the Target System
- E.7 Physical Dimensions for the 14-Pin Emulator Connector
- E.8 Emulation Design Considerations
- Glossary
- Index
Controlling and Resetting the Port
10-10
10.3.2 I/O Status Register (IOSR)
The IOSR returns the status of the asynchronous serial port and of I/O pins
IO0–IO3. The IOSR is a 16-bit, on-chip register mapped to address FFF6h in
I/O space. Figure 10–4 shows the fields in the IOSR, and bit descriptions fol-
low the figure.
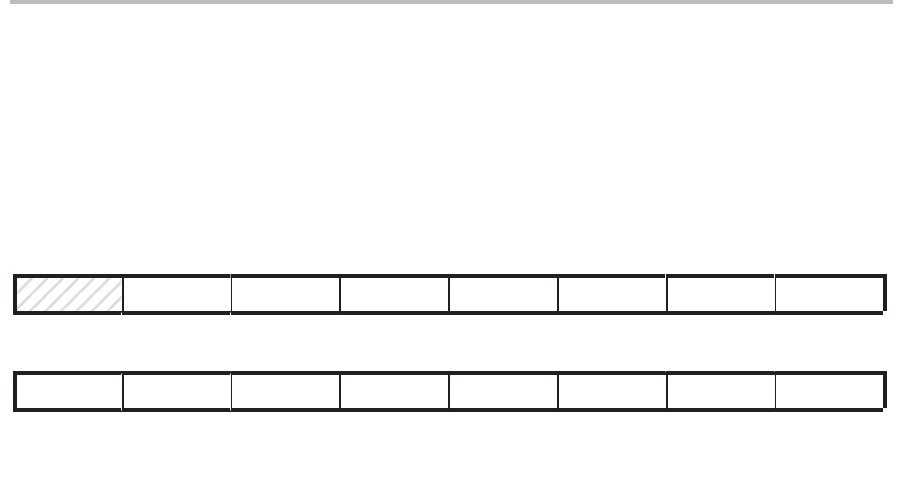
Figure 10–4. I/O Status Register (IOSR) — I/O-Space Address FFF6h
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Reserved ADC BI TEMT THRE FE OE DR
0 R/W1C–0 R/W1C–0 R–1 R–1 R/W1C–0 R/W1C–0 R–0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
DIO3 DIO2 DIO1 DIO0 IO3 IO2 IO1 IO0
R/W1C–x R/W1C–x R/W1C–x R/W1C–x R/W
†
–x R/W
†
–x R/W
†
–x R/W
†
–x
Note: 0 = Always read as 0; R=Read access; W1C=Write 1 to this bit to clear it to 0; W = Write access;
value following dash (–) is value after reset (x means value not affected by reset).
†
This bit can be written to only when it is configured as an output by the corresponding CIO bit in the ASPCR.
Bit 15 Reserved. Always read as 0.
Bit 14 ADC —
A
detect complete bit. If the CAD bit of the ASPCR is 1 and the
character
A
or
a
is received in the ADTR, ADC is set to 1. The character
A
or
a
remains in the ADTR after it has been detected. To avoid an overrun er-
ror when the next character arrives, the ADTR should be read immediately
after ADC is set.
ADC = 0
A
or
a
not has not been detected. No receive interrupt
(TXRXINT) will be generated.
ADC = 1
A
or
a
has been detected. If the CAD bit of the ASPCR is also
1, a receive interrupt (TXRXINT) will be generated, regardless
of the values of the DIM, TIM, and RIM bits of the ASPCR. For
as long as ADC = 1 and CAD = 1, a receive interrupt will occur.
Bit 13 BI — Break interrupt indicator. BI = 1 indicates that a break has been de-
tected on the RX pin. Write a 1 to this bit to clear it to 0. BI is also cleared to
0 at reset.
A break on the RX pin also generates an interrupt (TXRXINT).
Bit 12 TEMT — Transmit empty indicator. TEMT = 1 indicates whether the trans-
mit register (ADTR) and/or transmit shift register (AXSR) are full or empty.
This bit is set to 1 on reset.
TEMT = 0 The ADTR and/or AXSR are full.
TEMT = 1 The ADTR and the AXSR are empty; the ADTR is ready for a
new character to transmit.










