User Guide
Table Of Contents
- 1 Get to Know Your Device
- 2 Quick Internet Setup
- 3 Layout
- 4 Status
- 5 Internet Settings
- 6 Wireless Settings
- 7 Bandwidth Control
- 8 MAC Address Filter
- 9 IP-MAC Binding
- 10 Port Forwarding
- 11 DDNS
- 12 DMZ Host
- 13 UPNP
- 14 Administration
- Appendix
11 DDNS
In DDNS part, you can add DDNS rules.
DDNS maps the WAN IP address (public IP address) of the router to a domain name for dynamic domain name
resolution. This ensures proper operation of functions that involve the WAN IP address of the router, such as the
port forwarding function.
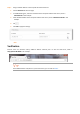
Choose Advanced to enter the page. By default, the function is disabled. Select Enable and the page is as follows:
Parameters
Parameters
Description
DDNS
It specifies whether to enable the DDNS function.
Service Provider
It specifies a DDNS service provider. The supported service providers include dyn.com,
oray.com and no-ip.com.
DDNS Username
It specifies the user name registered on a DDNS service provider's website for logging in
to the DDNS service.
DDNS Password
It specifies the password registered on a DDNS service provider's website for logging in
to the DDNS service.
Domain Host Name
It specifies the DDNS domain name register on a DDNS service provider's website.
Connection Status
It indicates the current status of the DDNS service.
11.1 Adding a DDNS Rule
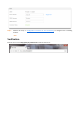
Step 1 Choose Advanced to enter the page.
Step 2 DDNS: Select Enable.