User's Manual
GL865 Hardware User Guide
1vv0300910 Rev.1 – 2011-07-22
Reproduction forbidden without Telit Communications S.p.A. written authorization - All Rights Reserved
page 60 of 79
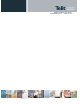
Drawing of the Magnetic Buzzer.
The disk and diaphragm are attracted to the core by the magnetic
field. When an oscillating signal is moved through the coil, it
produces a fluctuating magnetic field which vibrates the
diaphragm at a frequency of the drive signal. Thus the sound is
produced relative to the frequency applied.
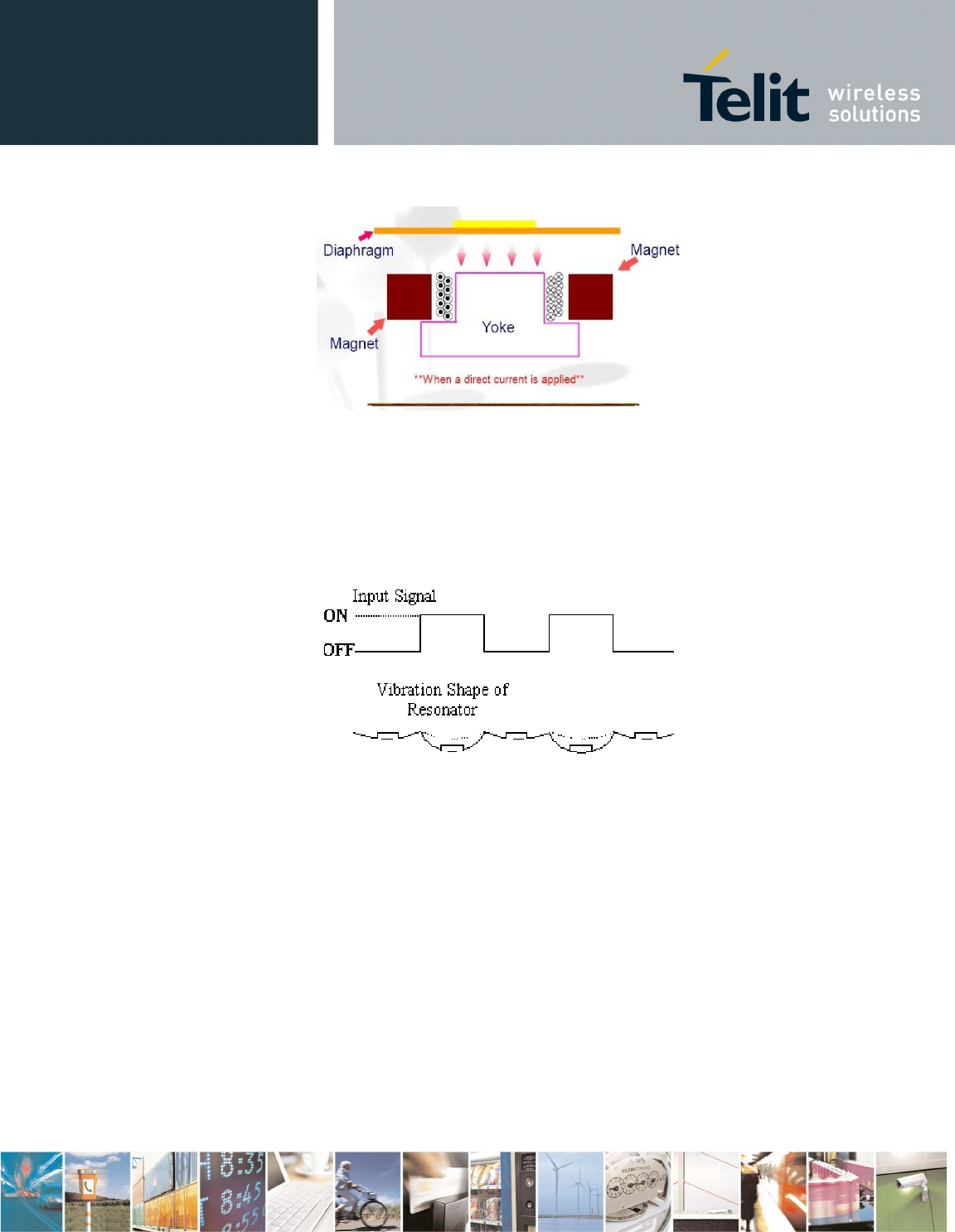
Diaphragm movement.
11.7.1. Frequency Behaviour
The frequency behaviour represents the effectiveness of the
reproduction of the applied signals. Because performance is
related to a square driving waveform (whose amplitude varies
from 0V to V
pp
), if you modify the waveform (
e.g. from square to
sinus
) the frequency response will change.
11.7.2. Power Supply Influence
Applying a signal whose amplitude is different from that
suggested by the manufacturer, the performance change following
the rule “if resonance frequency f
o
increases, amplitude
decreases”.