User manual
Table Of Contents
- Introduction
- Resources
- Notational Conventions
- Part 1: Making the Remote Connection
- Understanding Remote Control Layers
- Software Tools for Remote Control
- Connecting via ENET
- Connecting via USBTMC
- Connecting via GPIB
- Connecting via LSIB
- Configuring DCOM Connections
- Testing the Remote Connection
- Remote Control Assistant
- ActiveDSO
- VISA
- WaveStudio
- Part 2: Automation Programming Reference
- Automation Overview
- XStreamBrowser
- Viewing XStreamDSO Objects
- VBS Command
- Approach 1: Control from XStreamBrowser
- Approach 2: Program in VBS
- Approach 3: Program Using ActiveDSO
- Approach 4: Program Using VISA
- Control Variables
- Result Interfaces
- Synchronization
- Application Interactions
- Early and Late Binding
- Automation Programming Conventions
- Using Programming Variables
- Automation in MATLAB
- Automation in Python
- Automation in C#
- Part 3: Automation Control Variable Reference
- app
- app.Acquisition
- app.Acquisition.Cn
- app.Acquisition.Trigger
- app.Cursors
- app.CustomDSO
- app.Display
- app.Hardcopy
- app.History
- app.LabNotebook
- app.LogicAnalyzer
- app.Math
- app.Math.Fn and app.Math.XY
- app.Measure
- app.Measure.Pn
- app.Memory
- app.Memory.Mn
- app.PassFail
- app.PassFail.Qn
- app.Preferences
- app.ProbesCal
- app.SpecAnalyzer
- app.SaveRecall
- app.SaveRecall.Remote
- app.SaveRecall.Setup
- app.SaveRecall.Table
- app.SaveRecall.Utilities
- app.SaveRecall.Waveform
- app.TriggerScan
- app.Utility
- app.WaveScan
- app.WebEditor
- app.Zoom
- Part 4: Automation Result Interface Reference
- Base
- BinPopulations
- Bins
- BinWidth
- BusName
- CellType
- CellValue
- Columns
- DataArray
- ExtendedStatus
- FirstEventTime
- FirstPopulatedBin
- HorizontalFrameStart
- HorizontalFrameStop
- HorizontalOffset
- HorizontalPerColumn
- HorizontalPerStep
- HorizontalResolution
- HorizontalUnits
- HorizontalVarianceArray
- HorizontalVariances
- IndexOfFirstSampleInFrame
- LastEventTime
- LastPopulatedBin
- Levels
- LineAliasName
- LineName
- Lines
- Max
- MaxPopulation
- MaxPopulationBin
- MaxPopulationInRectangle
- Mean
- Min
- NumFrameDimensions
- NumSamplesInFrame
- OffsetAtLeftEdge
- Peaks
- PeakInfo
- PopulationInside
- PopulationOfRectangle
- PopulationOver
- PopulationUnder
- RMS
- Rows
- Samples
- Sdev
- Status
- StatusDescription
- Sweeps
- Top
- UniformInterval
- UpdateTime
- Value
- ValueArray
- VerticalFrameStart
- VerticalFrameStop
- VerticalMaxPossible
- VerticalMinPossible
- VerticalOffset
- VerticalPerRow
- VerticalPerStep
- VerticalResolution
- VerticalUnits
- XFrameStart
- XFrameStop
- XMaxPossible
- XMinPossible
- XOffset
- XPerStep
- XResolution
- XUnits
- YFrameStart
- YFrameStop
- YMaxPossible
- YMinPossible
- YOffset
- YPerStep
- YResolution
- YUnits
- Part 5: IEEE 488.2 Programming Reference
- GPIB Overview
- Interface Definitions
- IEEE 488.1 Standard Messages
- Program Message Format
- Data Types
- Response Messages
- I/O Buffers
- Making Service Requests
- Taking Instrument Polls
- Timing and Synchronization
- Waveform Transfer
- Part 6: IEEE 488.2 Command Reference
- Commands and Queries by Short Form
- Commands and Queries by Subsystem
- ACQUISITION Commands and Queries
- ARM_ACQUISITION, ARM
- AUTO_SETUP, ASET
- ATTENUATION, ATTN
- BANDWIDTH_LIMIT, BWL
- COMBINE_CHANNELS, COMB
- COUPLING, CPL
- FORCE_TRIGGER, FRTR
- INTERLEAVED, ILVD
- MEMORY_SIZE, MSIZ
- OFFSET, OFST
- REFERENCE_CLOCK, RCLK
- SAMPLE_CLOCK, SCLK
- SEQUENCE, SEQ
- STOP
- TIME_DIV, TDIV
- TRIG_COUPLING, TRCP
- TRIG_DELAY, TRDL
- *TRG
- TRIG_LEVEL, TRLV
- TRIG_MODE, TRMD
- TRIG_PATTERN, TRPA
- TRIG_SELECT, TRSE
- TRIG_SLOPE, TRSL
- VOLT_DIV, VDIV
- WAIT
- AUTOMATION Commands and Queries
- COMMUNICATION Commands and Queries
- CURSOR Commands and Queries
- DISPLAY Commands and Queries
- FUNCTION Commands and Queries
- HARDCOPY Commands and Queries
- MISCELLANEOUS Commands and Queries
- PROBE Commands
- SAVE/RECALL SETUP Commands and Queries
- STATUS Commands and Queries
- STORAGE Commands and Queries
- WAVEFORM TRANSFER Commands and Queries
- DISK DRIVE ANALYSIS (Option) Commands and Queries
- DD_ANALOG_COMP_THRESH, DACT
- DD_ANALYZE_REGION_DISABLE, DARD
- DD_ANALYZE_REGION_LENGTH, DARL
- DD_ANALYZE_REGION_START, DARS
- DD_BITCELL, DBIT
- DD_BYTE_OFFSET, DBYT
- DD_BYTE_OFFSET_SEGMENT, DSEG
- DD_CTAF_3DB, D3D
- DD_CTAF_BOOST, DBST
- DD_CTAF_FC, DDFC
- DD_CTAF_GROUP_DELAY, DFGD
- DD_ENCODING, DENC
- DD_ERR_INFO?, DERI?
- DD_ERR_NUM, DERR
- DD_FIND_BITCELL?, DFBIT?
- DD_FIND_ERROR, DFER
- DD_FIND_METHOD, DDFM
- DD_FIR, DFIR
- DD_FIR_ENABLE, DFEN
- DD_HEADSIGNAL_CHANNEL, DHSC
- DD_IGNORE_SAMPLES, DIGS
- DD_ML_MIN_SPACING, DRLM
- DD_ML_RUN_LENGTH_LIMIT, DRLE
- DD_NUM_ERRORS?, DNER?
- DD_OVERLAP_REF, DOVL
- DD_PES_ANALYSIS, DPA
- DD_PES_DATA?, DPD?
- DD_PES_SUMMARY_DATA?, DPSD?
- DD_READ_GATE_POLARITY, DRGP
- DD_READCLOCK_CHANNEL, DRCC
- DD_READGATE_CHANNEL, DRGC
- DD_RESET_AVERAGE, DRAV
- DD_SAM_THRESH, DST
- DD_SAMPLE_PHASE, DSPH
- DD_SHOW_FILTERED, DSF
- DD_SHOW_LEVELS, DSLV
- DD_SHOW_ML, DSML
- DD_SHOW_SAMPLE_TIMES, DSST
- DD_SIGNAL_INPUT, DDSI
- DD_SIGNAL_TYPE, DSIG
- DD_START_AVERAGING, DSAV
- DD_STORE_REFERENCE, DSTR
- DD_TRAIN_FILTER?, DTF?
- DD_VCO_SYNCH_PATTERN, DVSP
- DD_VCOSYNCH_TO_DATA, DVTD
- ET-PMT (Option) Commands and Queries
- Blank Page
Part 2: Automation Programming Reference
Approach 1: Control from XStreamBrowser
When a PC has a DCOM connection to a networked oscilloscope, a copy of XStreamBrowser running on
the PC has the same read/write capabilities as the version that is running locally on the oscilloscope. The
oscilloscope's entire XStreamDSO object hierarchy is exposed and editable from XStreamBrowser. This is
perhaps the simplest way to remotely control the oscilloscope.
This exercise modifies the oscilloscope channel C1 Vertical Scale setting directly from XStreamBrowser
installed on the PC.
Make the Connection
1. Connect the oscilloscope to your LAN, or directly to the PC using a cross-over cable.
2. Turn on the oscilloscope and go to Utilities > Utilities Setup > Remote and choose control from
TCP/IP.
3. Create a DCOM connection to the oscilloscope.
4. Download and install a copy of XStreamBrowser on the PC.
5. Open XStreamBrowser on the PC and connect to the oscilloscope.
6. When the oscilloscope appears in the Devices list, click on it to show the application hierarchy.
Find and Modify the Object
The Vertical settings associated with channels are part of the Acquisition subsystem, as they control the
characteristics of the ADCs at the input, directly affecting acquisition.
Since we're looking to modify a setting that affects the Acquisition subsystem, expand the Acquisition
folder to display the C1 object. Select the C1 object folder so that the C1 CVARs appear in the right-hand
window pane.
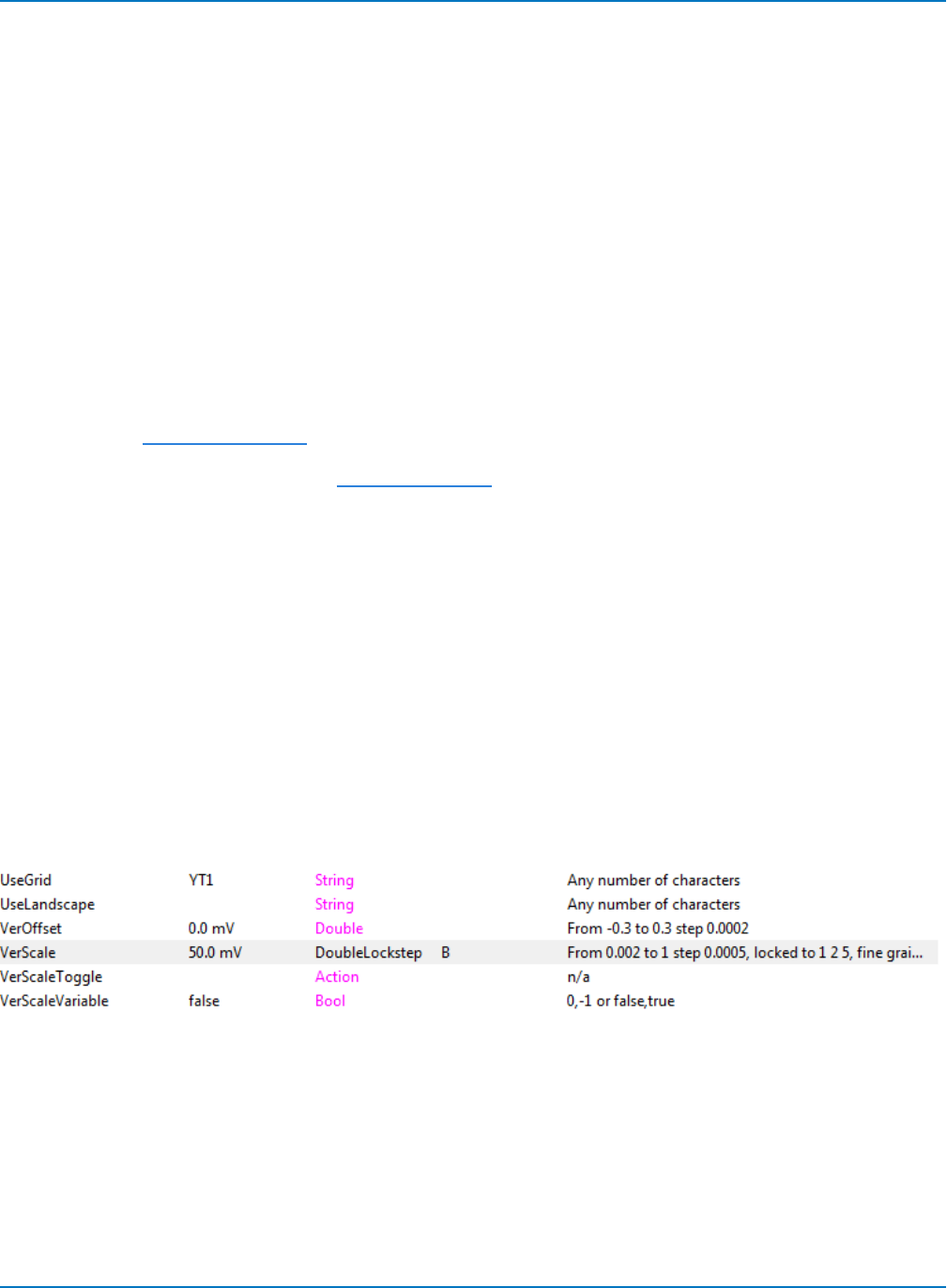
As you scroll down, you'll see the VerScale CVAR, showing whatever value was last set for that channel on
the oscilloscope, in this example, 50.0 mV.
XStreamBrowser tell us the following about this control:
l The Type column shows it is a DoubleLockstep
l The Flags/Status column shows B, meaning it is Backwards and incrementing the CVAR will
decrease the value.
2-11










