Hardware Instruction Manual
Table Of Contents
- Introduction
- Deciding on an OS
- Preparing for installation
- Installation
- Setup Tweaks – Things to Do During the Install
- System Performance Tweaks – Stuff to Do After Installing
- Windows Messenger
- Display properties
- Windows Sounds
- System Restore
- Performance
- Virtual memory
- Fast user switching
- Auto Start and System Services
- Disk I/O Performance Logging
- Write Behind Caching
- UDMA/ATA Mode for Hard Drives
- Separate Drives – How and Where
- Defrag Often
- Virus and other Utilities
- PlugIns and other Goodies
- XP and Win2000 Resources
17
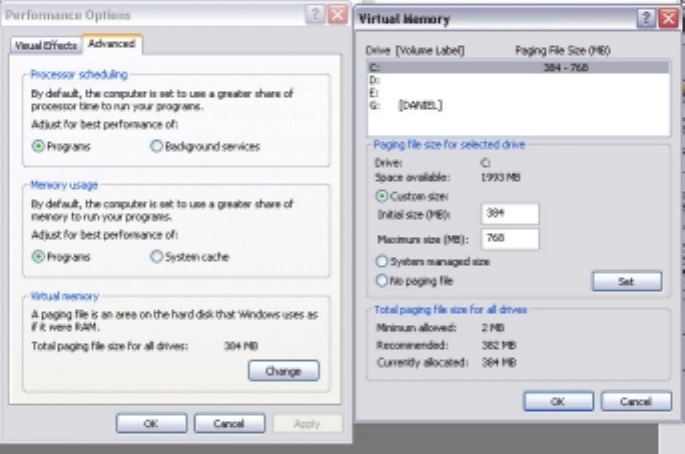
NOTE: Some users advise disabling virtual memory for increased performance. We do
not recommend this unless you have at least 512 MB of RAM. Even then, note that this is
not practical for all systems, as it can tend to make some machines less stable. That
said, if you choose to disable virtual memory you can do so on the same page (Control
Panel/System/Advanced).
Fast user switching
Windows NT and 2000 introduced a new feature – multiple user logons. While mainly
intended for use in corporate networks (allowing multiple users to access the same
machine), it is also useful for creating multiple profiles (e.g., general use, audio-optimized,
etc).
Windows XP takes the multiple users concept a step further, allowing for fast switching
between user profiles without logging off the first user. (The applications in use by the first
user will remain active until that user logs off, or until the computer is shut down.) While
this is a great feature for large corporate networks, it’s a big resource hog for your audio
Figure 11 – Setting Virtual Memory