User's Guide
Tarvos User Guide - Version 0.3 22
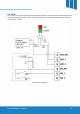
a. DIO Control
Here are some key control “dio” namespace variables in the TSI CLI:
dio.in.[1|2]
dio.out.[1|2]
dio.trigger_high.[1|2]
dio.trigger_low.[1|2]
The dio.in commands allow clients to monitor the inputs by polling for their values. The dio.out commands
allow the state of the digital outputs to be set. All with TSI CLI commands via the command channel.
The dio.trigger commands allow clients to setup automatic operating modes of the reader based upon a
change of state of an input. A change of an input from high to low or from low to high can be used to
automatically put the reader into ‘standby’ or ‘active’ mode.
b. DIO Monitor
event.dio.[1|2] value=[0|1] time=<time>
event.configuration.change name=dio.out.[1|2] newvalue=[0|1] oldvalue=[0|1|None]
Whenever a DIO input value changes state, the reader will send out an event with information as to the
new value of the input as well as the exact timestamp from the reader.
“event.dio.1 value=0 time=2017-11-10T10:06:57.710\r\n\r\n”
The reader also sends out configuration change events any time a variable changes state. This can be used
to also monitor when a DIO output event occurs from the reader.
“event.configuration.change name=dio.out.2 newvalue=1 oldvalue=None time=2017-11-
10T10:05:23\r\n\r\n”
5.7 Tag Operations
Beyond putting the reader into ‘active’ mode and monitoring the event channel for interrogated tags, the
reader can perform the tag operations suggested by the commands below.
tag.read_access_pwd()
tag.read_id()
tag.read_kill_pwd()
tag.read_tid()
tag.read_user_data()
tag.unlock()
tag.lock()
tag.write_access_pwd()
tag.write_id()
tag.write_kill_pwd()
tag.write_tid()