Codec C90 Administrator Guide
Table Of Contents
- Introduction
- Getting started
- About the menus
- The Settings menu
- Administrator Settings Library
- Description of the administrator settings
- The Audio settings
- The Camera settings
- The Conference settings
- The Do not disturb setting
- The H323 Profile settings
- The Network settings
- The Camera settings
- The Phone book server settings
- The Provisioning settings
- The Serial port settings
- The SIP Profile settings
- The Standby settings
- The System unit settings
- The Time zone setting
- The Video settings
- The Experimental menu
- Description of the administrator settings
- Cameras
- Appendices
- General room guidelines
- Guidelines for the executive meeting room
- Guidelines for the high end meeting room
- The Video Input Matrix
- Software upgrade
- Upload certificates
- XML files
- Log files
- NTP Time Zone expressions
- Supported RFCs in SIP
- TANDBERG Remote Control TRC5
- TANDBERG Remote Control TRC5 key map
- The PrecisionHD camera
- CE Declaration for Codec C90
- China RoHS table
- TANDBERG Codec C90 dimensions
- PrecisionHD 1080p camera dimensions
- PrecisionHD camera dimensions
- Technical specifications
D14129.02—NOVEMBER 2008
49
Codec C90
Administrator Guide
Contents Introduction Getting started About the menus About the settings Settings Library Cameras Appendices Contact us
Appendices
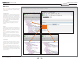
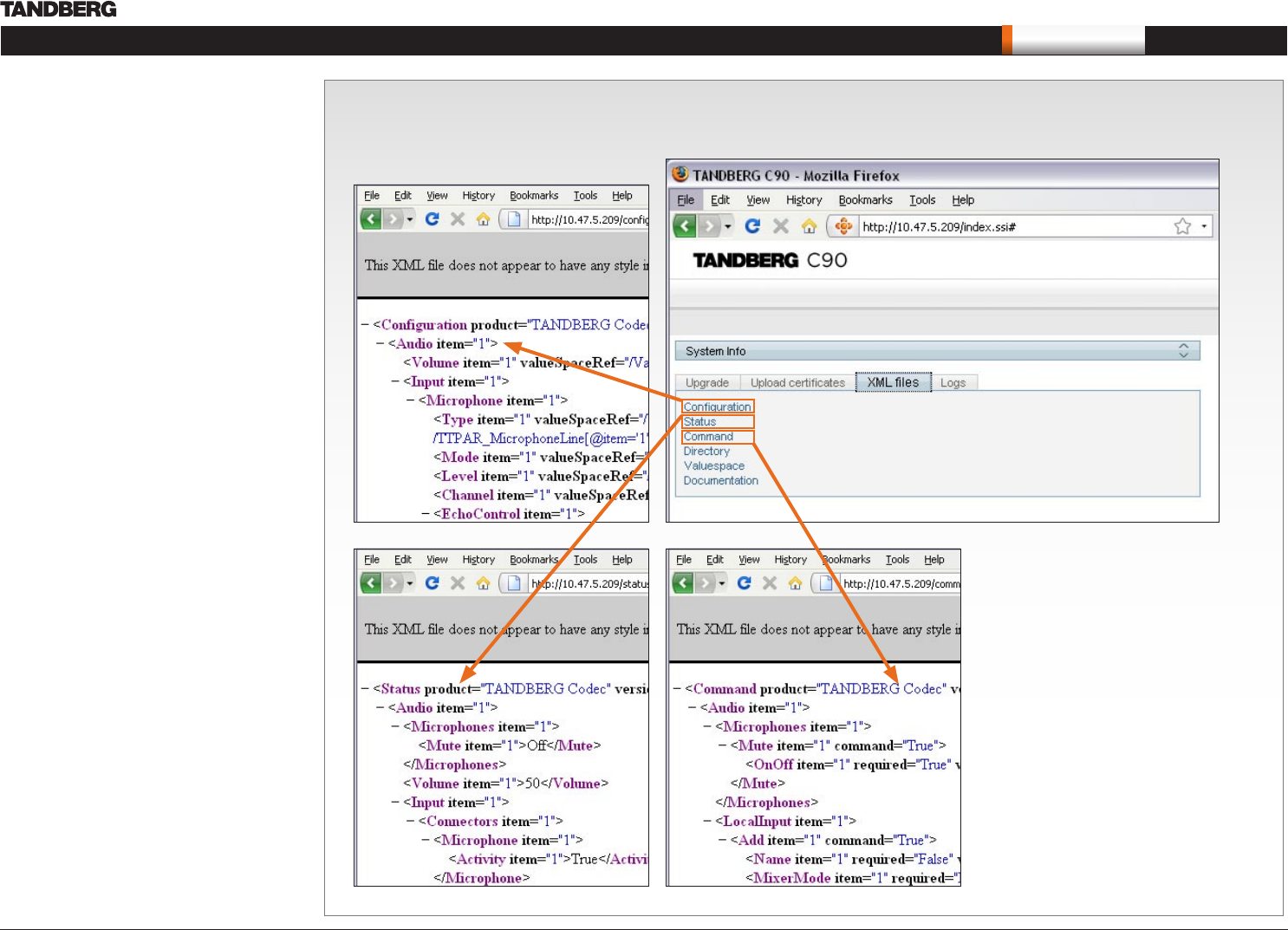
View XML files
Select the XML file to see a tree structure of all the configuration commands
XML files
The XML files tab gives a complete overview of the
status of the system and the commands available
on XML format.
Configuration
Configuration type commands defines the system
settings and are controlled from the Administrator
Settings menu or from the API. Configuration type
commands are either supplied or read by the user.
Example: Set IP addresses, default presentation
source, standby delay, and enabling/disabling of
various features etc.
The configuration commands are structured in
a hierarchy, making up a database of system
settings.
Status
Status type commands returns information about
the system and system processes and are issued
from the API. Status type commands are read by
the user.
Example: Information generated by the system
about ongoing calls, network status, conference
status etc.
All status information is structured in a hierarchy,
making up a database constantly being updated by
the system to reflect system and process changes.
Command
Command type commands instructs the system
to perform an action and are issued from the API.
Command type commands are supplied by the
user.
Example: instructing the system to place a call,
mute/unmute microphones, disconnect a call, etc.
A Command type command is usually followed by
a set of parameters to specify how the given action
is to be executed.