User Manual Part 3
Table Of Contents
- Introduction
- 1.1 New Features
- 1.2 Feature Overview
- 1.2.1 Single or Dual Mode Radio Options
- 1.2.2 Separate LAN and WAN Ports
- 1.2.3 Multiple Mounting Options
- 1.2.4 Antenna Support for 2.4 GHz and 5.2 GHz Radios
- 1.2.5 Sixteen Configurable WLANs
- 1.2.6 Support for 4 BSSIDs per Radio
- 1.2.7 Quality of Service (QoS) Support
- 1.2.8 Industry Leading Data Security
- 1.2.9 VLAN Support
- 1.2.10 Multiple Management Accessibility Options
- 1.2.11 Updatable Firmware
- 1.2.12 Programmable SNMP v1/v2/v3 Trap Support
- 1.2.13 Power-over-Ethernet Support
- 1.2.14 MU-MU Transmission Disallow
- 1.2.15 Voice Prioritization
- 1.2.16 Support for CAM and PSP MUs
- 1.2.17 Statistical Displays
- 1.2.18 Transmit Power Control
- 1.2.19 Advanced Event Logging Capability
- 1.2.20 Configuration File Import/Export Functionality
- 1.2.21 Default Configuration Restoration
- 1.2.22 DHCP Support
- 1.2.23 Multi-Function LEDs
- 1.3 Theory of Operations
- Hardware Installation
- Getting Started
- System Configuration
- Network Management
- Configuring Access Point Security
- 6.1 Configuring Security Options
- 6.2 Setting Passwords
- 6.3 Enabling Authentication and Encryption Schemes
- 6.4 Configuring Kerberos Authentication
- 6.5 Configuring 802.1x EAP Authentication
- 6.6 Configuring WEP Encryption
- 6.7 Configuring KeyGuard Encryption
- 6.8 Configuring WPA Using TKIP
- 6.9 Configuring WPA2-CCMP (802.11i)
- 6.10 Configuring Firewall Settings
- 6.11 Configuring VPN Tunnels
- 6.12 Configuring Content Filtering Settings
- 6.13 Configuring Rogue AP Detection
- 6.14 Configuring User Authentication
- Monitoring Statistics
- Command Line Interface Reference
- Configuring Mesh Networking
- Technical Specifications
- Usage Scenarios
- Customer Support
- Index
Configuring Mesh Networking
9-35
21. Now a QoS policy needs to be defined for the shipping and receiving mesh WLAN. The IT
Team still envisions little (if any) video or voice traffic within the shipping as the MUs within
primarily scan bar codes and upload data. This holds true for the QoS requirements for AP3
and AP4 as the required coverage area has grown, not the security, access permission or
QoS considerations. For more information, see how the team defined the AP1 and AP2 QoS
policy starting on step 25 within Trion’s Initial Deployment on page 9-19.
The WLAN configuration has now been set for both AP3 and AP4. The team now needs to
define the radio configurations for AP3 and AP4.
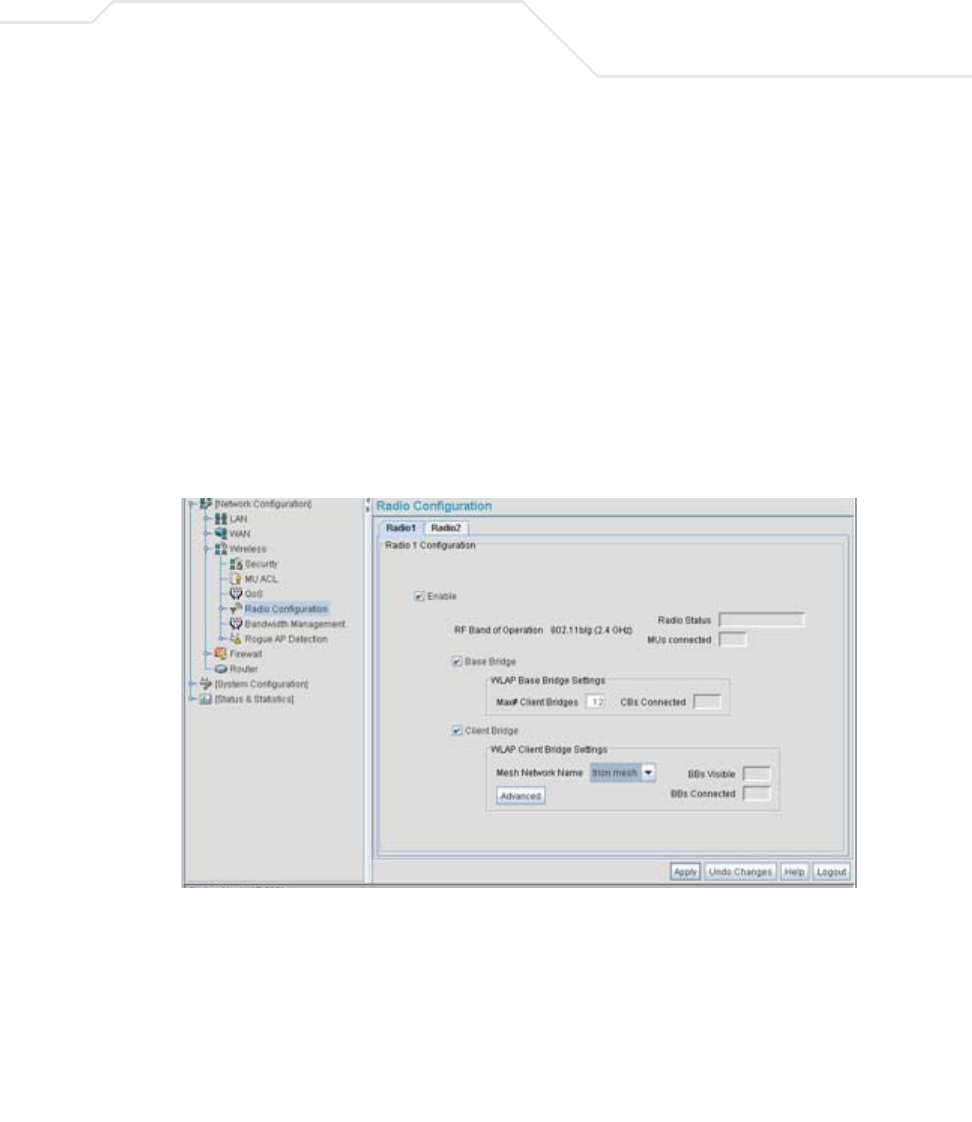
22. The IT team selects Network Configuration -> Wireless -> Radio Configuration from
the AP-5131 menu tree.
The Radio Configuration screen displays.
23. For both AP3 and AP4, the IT Team enables Radio 1 and defines the radio as a repeater
(enabling each radio as both a base and client bridge).
Both AP3 and AP4 are intended to pass along mesh network back data to AP1 and support
the 802. 11b/g MUs within the shipping yard.
24. The IT Team leaves each radio’s Max # Client Bridge setting at the default setting of 12.
This ensures as client bridges are added to the growing mesh network that they can be
accounted for.
25. For both AP3 and AP4, the IT Team uses the Mesh Network Name drop-down menu to
assign the “trion mesh” WLAN to radio 1. This is the WLAN the AP3 and AP4 radios will
use to interoperate with the MUs populating the shipping yard.










