User Manual
49
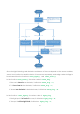
response program to let the car move backwards in the opposite direction (3), and then turn back
to the original direction until a black line is detected again and move forward (4).
Code Explanation
The logic of the code is just as shown in the flow chart above.
Three Python modules are used in the code, including the imported
SunFounder_Line_Follower, front_wheels, and back_wheels. They are the drivers for this kit,
respectively for line following , front wheels, and rear wheels
The related classes have been defined here. When the modules are applied to use, objects
will be created for related classes, and different parts of hardware will be driven by calling a
function by the class object.
Similar to the line following module, we create an object named lf:
lf = Line_Follower_module.Line_Follower(references=REFERENCES)
The parameter is initial, and then we can apply the function by calling a class object.
lf.read_digital()
This function is used to read the analog signal of all probes, and convert it into digital signal. If
the signal is larger than the reference, the corresponding parameter will be 0; if it is lower than
the reference, the parameter will be 1. There are five probes, thus we will get a 5-parameter
list.
fw.turn(turning_angle)
The function for front wheels' turning. The main program will call this function if applying the
front wheels for turning. The parameter is the turning angle.
bw.forward()
bw.set_speed(forward_speed)
Here we need two functions for rear wheels. One is to control the rotating direction as forward
(for rotating backwards, bw.backward()). The second one is to set the rotating speed; the
parameter is the speed value (range 0~100). The bigger the parameter is, the faster the wheel
rotates.