Datasheet
Electrical characteristics STM32F100xC, STM32F100xD, STM32F100xE
74/98 Doc ID 15081 Rev 7
Figure 27. I/O AC characteristics definition
5.3.15 NRST pin characteristics
The NRST pin input driver uses CMOS technology. It is connected to a permanent pull-up
resistor, R
PU
(see Ta ble 43 ).
Unless otherwise specified, the parameters given in Ta bl e 46 are derived from tests
performed under the ambient temperature and V
DD
supply voltage conditions summarized
in Ta bl e 9 .
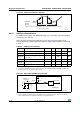
Figure 28. Recommended NRST pin protection
1. The reset network protects the device against parasitic resets.
2. The user must ensure that the level on the NRST pin can go below the V
IL(NRST)
max level specified in
Table 46. Otherwise the reset will not be taken into account by the device.
ai14131
10%
90%
50%
t
r(IO)out
OUTPUT
EXT ERNAL
ON 50pF
Maximum frequency is achieved if (t
r
+ t
f
) 2/3)T and if the duty cycle is (45-55%)
10 %
50%
90%
when loaded by 50pF
T
t
r(IO)out
Table 46. NRST pin characteristics
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
V
IL(NRST)
(1)
1. Guaranteed by design, not tested in production.
NRST Input low level voltage –0.5 0.8
V
V
IH(NRST)
(1)
NRST Input high level voltage 2 V
DD
+0.5
V
hys(NRST)
NRST Schmitt trigger voltage
hysteresis
200 mV
R
PU
Weak pull-up equivalent resistor
(2)
2. The pull-up is designed with a true resistance in series with a switchable PMOS. This PMOS contribution to
the series resistance must be minimum
(~10% order).
V
IN
= V
SS
30 40 50 kΩ
V
F(NRST)
(1)
NRST Input filtered pulse 100 ns
V
NF(NRST)
(1)
NRST Input not filtered pulse 300 ns
DLG
670)[
5
38
1567
9
''
)LOWHU
,QWHUQDOUHVHW
)
([WHUQDO
UHVHWFLUFXLW