User Manual
Applications
RFI-9256 Radio Modem User Manual Page 38 of 96
5.4 Point-to-point Network with Back-to-back Repeaters
The final point-to-point configuration involves the addition of one or more back-to-back repeaters. Back-to-
back repeaters can be used to extend the range of an RFI-9256 based network.
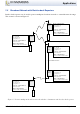
The basic network set-up for back-to-back repeaters in point-to-point links is shown in Figure 13.
RFI-9256
Master
RFI-9256
Repeater
Slave
Main
DTE
Main
DTE
RADIO CONFIGURATION
Unit is a SLAVE
Network Address: 1
Hopping Pattern: 20
Rx Address: 20
PROTOCOL CONFIGURATION
Main Port: Point-to-point to 1000
Aux Port: Point-to-point to 1000
SERIAL CONFIGURATION
Main Port: 115200, 8N1, Hardware Flow
Aux Port: 115200, 8N1, No Flow
RADIO CONFIGURATION
Unit is a MASTER
Network Address: 1
Hopping Pattern: 20
Rx Address: 1000
PROTOCOL CONFIGURATION
Main Port: Point-to-point to 20
Aux Port: Point-to-point to 20
SERIAL CONFIGURATION
Main Port: 115200, 8N1, Hardware Flow
Aux Port: 115200, 8N1, No Flow
RFI-9256
Repeater
Master
RFI-9256
Slave
Aux
DTE
RADIO CONFIGURATION
Unit is a SLAVE
Network Address: 1
Hopping Pattern: 30
Rx Address: 3000
PROTOCOL CONFIGURATION
Aux Port: Point-to-point to 20
SERIAL CONFIGURATION
Aux Port: 115200, 8N1, No Flow
Aux Null Modem Cable
Back-to-back Repeater
RADIO CONFIGURATION
Unit is a MASTER
Network Address: 1
Hopping Pattern: 30
Rx Address: 20
PROTOCOL CONFIGURATION
Aux Port: Point-to-point to 3000
SERIAL CONFIGURATION
Aux Port: 115200, 8N1, No Flow
Figure 13: Point-to-point network with a back-to-back repeater
In this scenario, the master 1 and slave 1 form the first network. A point-to-point connection is established
between both main and auxiliary ports of these two units. Data transmitted by DTE1 on master 1 will be
received on DTE1 of slave 1. Data transmitted by DTE2 on the master will be received by slave 1, and
passed to master 2 via a null modem cable linking the two auxiliary ports. This data is then re-transmitted to
slave 2, which outputs the received data on its auxiliary port.