Datasheet
Pin settings
VIPER06
4/28
DocID022794 Rev 2
3 Pin settings
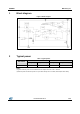
Figure 3: Connection diagram (top view)
The copper area for heat dissipation has to be designed under the DRAIN pins.
Table 2: Pin description
Pin
Name
Function
DIP-7
SSO10
1
1
GND
Connected to the source of the internal power MOSFET and
controller ground reference.
2
2
VDD
Supply voltage of the control section. This pin provides the charging
current of the external capacitor.
3
3
LIM
This pin allows setting the drain current limitation. The limit can be
reduced by connecting an external resistor between this pin and
GND. Pin left open if default drain current limitation is used.
4
4
FB
Inverting input of the internal transconductance error amplifier.
Connecting the converter output to this pin through a single resistor
results in an output voltage equal to the error amplifier reference
voltage (see V
FB_REF
in Table 6: "Supply section "). An external
resistor divider is required for higher output voltages.
5
5
COMP
Output of the internal transconductance error amplifier. The
compensation network has to be placed between this pin and GND
to achieve stability and good dynamic performance of the voltage
control loop. The pin is used also to directly control the PWM with
an optocoupler. The linear voltage range extends from V
COMPL
to
V
COMPH
(Table 6: "Supply section ").
7, 8
6-10
DRAIN
High-voltage drain pins. The built-in high-voltage switched startup
bias current is drawn from these pins too. Pins connected to the
metal frame to facilitate heat dissipation.