User Manual
RackPack: Premium Mic Pre
15
Even a voltage that has accidentally or through technical failure been
connected to a ground line cannot be transmitted. So transformers can
exclude even mishaps or problems in an installation reaching the cat-
egories “improbable” till “unbelievable” ...
Further, the phantom powering of microphones does not require any
condensers in the preamp socket which has further sonic advantages.
From our personal listening impression we can recommend transform-
ers in any case. The advantages in operational safety can not be over-
estimated especially in critical or complex installations for studio, live
or broadcast applications.
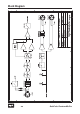
Stage 2 – The Discrete Differential Amplifier
From the input transformer, the signal is routed to a discrete differen-
tial amplifier based upon a quad parallel transistor circuitry. This paral-
lel circuit of eight single transistors reduces noise remarkably through
distribution of load.
The discrete differential amplifier is the central amplifying stage; here
the amount of the amplification is controlled by a current-carrying
source. Control systems that are triggered by current rather than volt-
age have the main advantage that possible negative effects of the po-
tentiometer will not affect the audio signal.
The discrete differential amplifier offers a maximum amplification of
up to 68 dB. A servo drive circuit actively eliminates DC offsets of the
differential amplifier. Servo drive circuitry minimizes DC offsets more
effectively than conventional solutions that utilize capacitors by set-
ting the DC offset to almost 0 mV. In addition, the active servo drive
solution has sonic advantages over passive capacitors as it tends to
produce less distortions.
Stage 2 – The Discrete Differential Amplier
Technology