User's Manual Part 1
Table Of Contents
- 1: Introduction
- 2: Product Overview
- 2.1 Introduction to the workflow interface
- 2.2 Product overview
- 2.3 General product handling and operation
- 2.3.1 Protection from water and dust ingress
- 2.3.2 Important battery charging note
- 2.3.3 Powering on/off
- 2.3.4 Attaching the strap
- 2.3.5 About the touchscreen display
- 2.3.6 Selecting the active interface
- 2.3.7 Running a function or test
- 2.3.8 Repeating a function or test
- 2.3.9 Screen title bar buttons/icons
- 2.3.10 Capturing a screen image (screenshot)
- 2.3.11 Stopping a test
- 2.3.12 Saving results
- 2.3.13 Maximum test duration for continuous tests
- 2.3.14 Interpreting results
- 2.4 Handling the MoCA/RF module
- 2.5 Remote control of the unit
- 2.6 Licensed feature details
- 2.7 Maintenance
- 2.8 FTP information
- 2.9 Technical support
- 3: Wi-Fi Testing Menu
- 4: 10/100/1G Testing Menu
- 5: System Menu
- 5.1 Record Manager
- 5.2 Admin Port
- 5.3 Set Date and Time
- 5.4 Version Info
- 5.5 Battery Status
- 5.6 Video
- 5.7 Cal Touchscreen
- 5.8 Licensed Options
- 5.9 Update Firmware
- 5.10 System/Module Settings
- 5.10.1 System/Module Settings > Base Unit
- 5.10.2 System/Module Settings > RF Video Module
- 5.10.3 System/Module Settings > ADSL/VDSL2 Module
- 5.10.4 System/Module Settings > Combined Module Default
- 5.10.5 System/Module Settings > MoCA Module
- 5.10.6 System/Module Settings > DOCSIS Module
- 5.10.7 System/Module Settings > CSM Module
- 5.10.8 System/Module Settings > MoCA-RF Module
- 5.10.9 System/Module Settings > Wi-Fi
- 5.11 Signature Capture
- 5.12 Language Selection
- 5.13 Help and Support
- 5.14 System Information
- 5.15 Wizard GUI
Tech-X Flex
®
(NG2) Tech-X Flex User Guide - Firmware v06.50
2-49
Intro
Overview
Wi-Fi
Ethernet
System
IP/Video
MoCA
RF
Specs
In this case, the traffic is VNC and the host is the unit, whose VNC server expects traffic on port 5900.
During the Enable WAN Remote Control step, the unit configures the router to accept traffic on some
other port (as reported for External VNC Port) and forward the traffic to its LAN address on port 5900. In
this way, the unit appears to the VNC client as any other host on the internet and full VNC functionality is
supported. Note that this general methodology is commonly used by other devices such as internet-
based gaming systems, where non-public hosts must communicate with one another across the internet.
These systems automatically configure their respective routers much like the unit.
With respect to the persistence of the router configuration, note the following:
• If you never manually undo the router configuration (Disable WAN Remote Control), the forwarding
path may remain indefinitely. This may or may not be of concern. While it represents a path through
the firewall that did not exist previously, its scope is limited to traffic on port 5900 reaching the
address that the unit was using during the VNC session. A network administrator should provide
advice and procedures related to this possibility.
•The Disable WAN Remote Control setting is always enabled, in the event that it must be executed
some time in the future, perhaps some time after the end of the VNC session.
• Port forwarding can be manually configured through the administrative interface of a router. If you
use this interface to make changes to settings that were configured by the unit, the Disable WAN
Remote Control function may fail afterwards. Therefore, it is strongly recommended to allow the unit
to perform all router configuration tasks and to use the router interface only if absolutely necessary.
The unit uses UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) technology when configuring the router. UPnP has other
applications as well. For more information, see http://www.upnp.org/.
2.5.4 Initiating a VNC connection on the client
To initiate a VNC connection and thus begin a remote control session, you must first:
1. Be sure that a functional VNC client is properly installed on the client device (see Installing a VNC
client (viewer) on page 2-34).
2. Establish IP connectivity with the unit in a manner suitable for VNC control (see Remote control setup
scenarios on page 2-43).
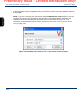
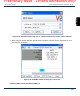
Once these steps are complete and you know the IP address assigned to the unit, you can initiate a VNC
session as follows:
Initiating a VNC session with RealVNC
Preliminary issue - Limited distribution only!