Data Sheet
18
Appendix A: Window Design Guide
A1: Optical Window Dimensions
To ensure that the performance of the APDS-9301 will not
be affected by improper window design, there are some
criteria requested on the dimensions and design of the
window. There is a constraint on the minimum size of the
window, which is placed in front of the photo light sensor,
so that it will not affect the angular response of the APDS-
9301. This minimum dimension that is recommended will
ensure at least a ±35° light reception cone.
If a smaller window is required, a light pipe or light guide
can be used. A light pipe or light guide is a cylindrical piece
of transparent plastic, which makes use of total internal
reflection to focus the light.
The thickness of the window should be kept as minimum
as possible because there is a loss of power in every optical
window of about 8% due to reflection (4% on each side)
and an additional loss of energy in the plastic material.
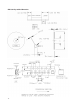
Figure A1 illustrates the two types of window that we
have recommended which could either be a flat window
or a flat window with light pipe.
Figure A1. Recommended Window Design
Table A1 and Figure A2 show the recommended dimen-
sions of the window. These dimension values are based
on a window thickness of 1.0mm with a refractive index
1.585.
The window should be placed directly on top of the light
sensitive area of APDS-9301 (see Figure A3) to achieve
better performance. If a flat window with a light pipe is
used, dimension D2 should be 1.55mm to optimize the
performance of APDS-9301.
Figure A2. Recommended Window Dimensions
WD: Working Distance between window front panel &
APDS-9301
D1: Window Diameter
T: Thickness
L: Length of Light Pipe
D2: Light Pipe Diameter
Z: Distance between window rear panel and
APDS-9301
All dimensions are in mm
Z
L
T
D1
Top View
APDS-9301
Photo Light Sensor
WD
D2 D1
D2