Data Sheet
SCL
SRN
VSYS
Coulomb
Bus
SDA
Counter
GPOUT
BIN
CPU
ADC
SRP
PACKP
Li -Ion
Cell
LDO
VDD
VSS
T
PACKN
Protection
IC
NFET
NFET
1.8 V
BAT
Battery Pack
I
2
C
0 47 µF
.
1 µF
bq27441-G1
SLUSBH1C –NOVEMBER 2013–REVISED DECEMBER 2014
www.ti.com
9 Detailed Description
9.1 Overview
The fuel gauge accurately predicts the battery capacity and other operational characteristics of a single Li-based
rechargeable cell. It can be interrogated by a system processor to provide cell information, such as state-of-
charge (SoC).
NOTE
The following formatting conventions are used in this document:
Commands: italics with parentheses() and no breaking spaces, for example, Control().
Data Flash: italics, bold, and breaking spaces, for example, Design Capacity.
Register bits and flags: italics with brackets [ ], for example, [TDA]
Data flash bits: italics, bold, and brackets [ ], for example, [LED1]
Modes and states: ALL CAPITALS, for example, UNSEALED mode.
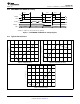
9.2 Functional Block Diagram
9.3 Feature Description
Information is accessed through a series of commands, called Standard Commands. Further capabilities are
provided by the additional Extended Commands set. Both sets of commands, indicated by the general format
Command), are used to read and write information contained within the control and status registers, as well as its
data locations. Commands are sent from system to gauge using the I
2
C serial communications engine, and can
be executed during application development, system manufacture, or end-equipment operation.
The key to the high-accuracy gas gauging prediction is Texas Instruments proprietary Impedance Track™
algorithm. This algorithm uses cell measurements, characteristics, and properties to create state-of-charge
predictions that can achieve high accuracy across a wide variety of operating conditions and over the lifetime of
the battery.
The fuel gauge measures the charging and discharging of the battery by monitoring the voltage across a small-
value sense resistor. When a cell is attached to the fuel gauge, cell impedance is computed based on cell
current, cell open-circuit voltage (OCV), and cell voltage under loading conditions.
The fuel gauge uses an integrated temperature sensor for estimating cell temperature. Alternatively, the host
processor can provide temperature data for the fuel gauge.
More details are found in the bq27441-G1 Technical Reference Manual (SLUUAC9).
10 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2013–2014, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: bq27441-G1