Datasheet
SPD series pressure sensor
last update
December 6, 2011
reference
SPD-dil family
page
4/5
Interfacing SPD pressure sensors to microcontrollers.
In general this kind if sensors based on Wheatstone bridges has to be connected to
microcontrollers. These can be done very easy with the Smartec’s Universal Transducer
Interface (UTI). Below the power of such a UTI system is explained. The list of advantages
must be clear to the designer:
• Simple, one chip hardware, just a UTI and the micro
• Thanks to the ratiometric measurement, UTI solution is independent of the
supply voltage, so no need for a precise power supply, or to worry about
power-supply drift (V
cc
of UTI is 3 – 5.5 V.)
• AC excitation which means no problems with offset drift of the input amplifier
and also AC prevents corrosion effects.
• In combination with the Smartec temperature sensor easy temperature
compensation can be realized.
For information and specifications of the UTI please go to the relevant datasheets in the
supportshop of our website.
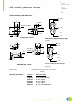
UTI excitation of bridges in voltage or current mode.
All the above given figures are based on excitation with a DC voltage (5 V.)
When, due to temperature changes, all of the four resistors change in the same way, this will have no
effect on the bridge output voltage. This is valid for the case that the bridge is supplied with voltage.
In the UTI we also have a current-mode supply (mode 11 and 12). When one of these modes are applied
the conversion of supply current to supply voltage depends on the bridge resistance, and therefore on
the resistor temperature coefficient. The current mode is applied to compensate also for another
temperature coefficient, which also exist in the voltage mode.
This temperature coefficient is due to the change in the mechanical properties of the membrane of the
pressure sensor and of the piezo-resistance effect. So, this figure given in this specification concerns
the mechanical and the electro-mechanical properties in total.
uti
UTI in Current mode(11,12) UTI in Voltage mode(9,10)
E
A
C
D
B
F
E
C
D
A
B
F
i
R
ref