User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Bridges Hardware Guide
- Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Deploying Silver Spring Networks Bridges
- A Specifications
- Overview
- eBridge and sBridge Features
- Silver Spring Networks eBridge Specifications
- Silver Spring Networks sBridge Specifications
- Regulatory Compliance - Module Certifications
- FCC Certification (Radiated/Conducted Emissions Compliance FCC Part 15.247)
- Industry Canada Certification (Radiated/Conducted Emissions Compliance RSS-210)
- C-Tick Level 3 (Radiated/Conducted Emissions Compliance AS/NZS4268, AS/NZS4778)
- Silver Spring Networks NIC, FCC IDs: OWS-NIC515 IC: 5975A-NIC515 (sBridge) OWS-NIC506, IC:5875A-NIC506 (eBridge)
- Glossary
- Index
Bridges Hardware Guide Silver Spring Networks 12
2 Deploying Silver Spring Networks Bridges
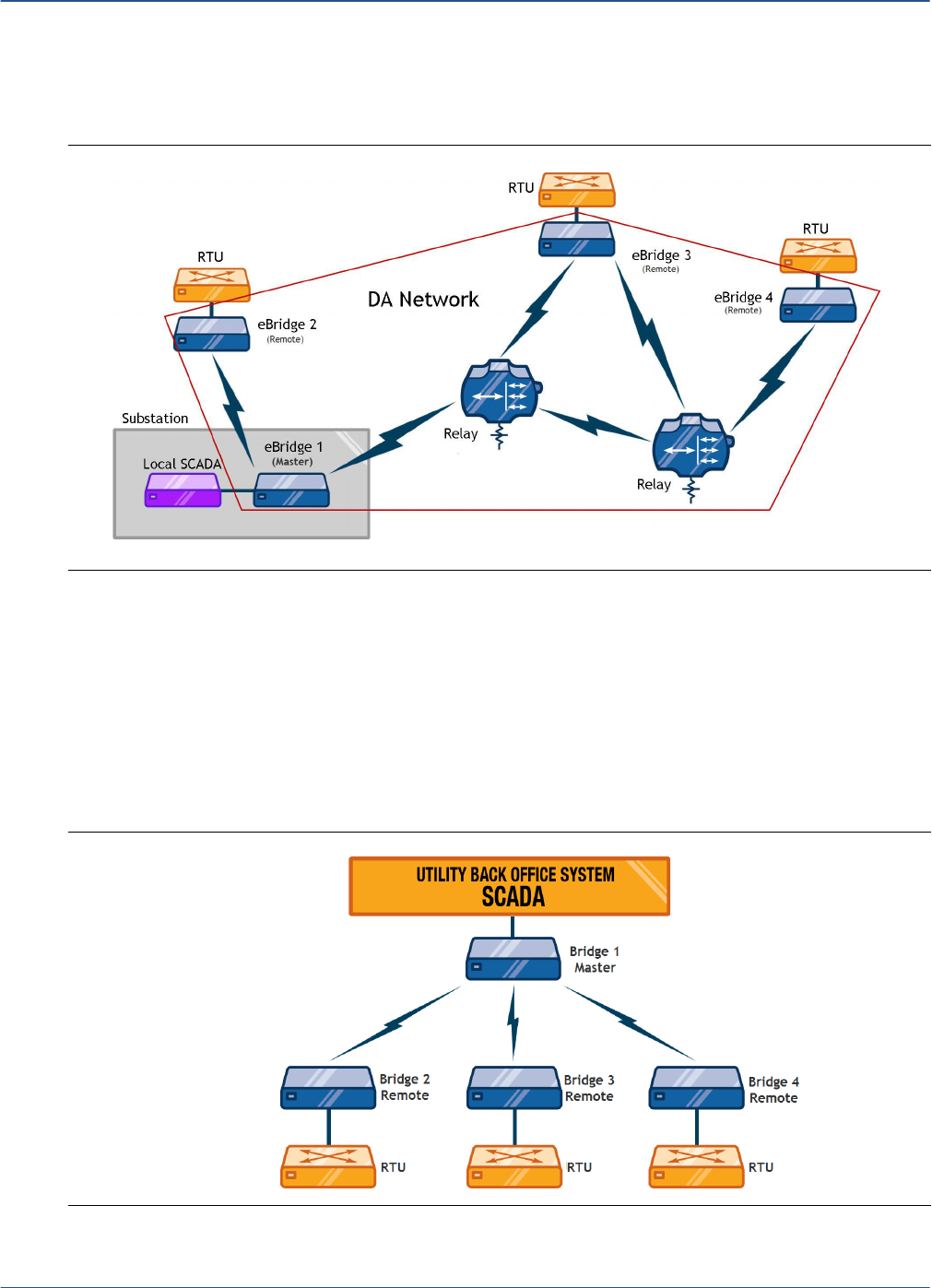
the DA (Distribution Automation) network, as indicated in Figure 5. Here, the pre-existing
electrical distribution grid is overlaid with the bridge-based DA network deployment.
Relays are used to extend the RF signal to greater distances and to extend the signal around
obstacles in the field.
Centralized and Decentralized Master/Remote Deployments
A Master/Remote deployment can be centralized or decentralized. In a centralized Master/
Remote deployment, the SCADA system resides at the back office and all data is drawn back to
the central location. This resembles the classic “star” network.
Figure 5. Master/Remote Example
Figure 6. Example of a Centralized Master/Remote Deployment










