Basic Documentation
122/256
Siemens Modular Heating Controller RMH760B CE1P3133en
Building Technologies 9 Heating circuit control 2017-09-29
9.5 Weather-compensated heating circuit control
The flow temperature setpoint of heating circuit control is determined by the heating
curve and other influencing factors.
The main reference variable of heating circuit control is the outside temperature. It can
be acquired by different devices:
• By the locally connected outside sensor
• Via bus from some other device
The controller delivers 3 different types of outside temperatures whereby heating
circuits 2 and 3 have access to their own outside temperature. The other applications
(heating circuit 1, pumps, boiler, demand transformers, etc.) share a common outside
temperature.
Depending on the type of building construction, the outside temperature acts on the
space with a certain delay. For this reason, the reference variable used by the heating
curve is not the actual but the composite outside temperature.
To determine the heating limit (summer / winter operation), the attenuated outside
temperature is also required (see below).
The heating curve is determined by the 2 curvepoints at the design temperature and
the theoretical heating limit. Heat transmission in the space is not linear, however.
When there is a small differential between flow temperature and room temperature, the
ability of heat transmission decreases. This is taken into account by the heating curve.
The setpoint predefined by the heating curve can also be influenced by the following
factors:
• The room temperature setpoint
• The current room temperature (room temperature influence)
For more detailed information, refer to subsection 9.5.3 "Influences on the flow
temperature setpoint".
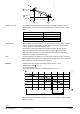
9.5.1 The composite and the attenuated outside temperature
Identifiers used:
TO
Actual outside temperature
TOeff
Composite (effectively acting) outside temperature
TOfil
Outside temperature filtered with the building time constant
TOstrDmp
Attenuated outside temperature
τBldg
Building time constant
p
Window
Proportion of windows in %
The composite outside temperature is made up of the actual outside temperature To
and the outside temperature TOfil filtered with the building time constant
τBldg. The
proportion of windows p
Window
(adjustable from 0…100 %) determines the proportions
with which the 2 temperatures are considered.
The composite outside temperature is used for the heating curve and the heating limit.
To obtain the attenuated outside temperature, the actual outside temperature TO is
filtered twice with the building time constant
τBldg.
Outside temperature
Composite outside
temperature
Attenuated outside
temperature
Heating curve
Other influences
Composite
outside
temperature
⇒
Attenuated outside
temperature