User Manual
6 / 20
Siemens Modulating refrigerant valves, PN 63 CE2N4717en
Smart Infrastructure 2019-11-25
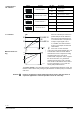
The 4-wire connection should always be given preference!
S
NA
P
MED
S
TR
P
TR
I
F
Wire cross-section [mm
2
]
1.5
2.5
4.0
2)
Product number
[VA]
[W]
[VA]
[W]
[A]
max. cable length L [m]
MVS661..N
32
12
≥50
≥40
1.6…4 A
65
110
160
MVS661..N
32
12
≥
50
≥
40
1.6…4 A
20
35
50
S
NA
= nominal apparent power for selecting the transformer
P
med
= Typical power consumption in the application
S
TR
= Minimum apparent transformer power
P
TR
= Minimum DC supply power
I
F
= Minimal Required slow fuse
L = max. cable length; with 4-wire connections, the max. permissible length of the separate 1.5 mm
2
copper positioning signal wire is 200 m
1)
All information at AC 24 V or DC 24V
2)
With 4 mm
2
electrical wiring reduce wiring cross-section for connection inside valve to 2.5 mm
2
.
Sizing
For straightforward valve sizing, refer to the tables for the relevant application (from
page 15).
For accurate valve sizing, we recommend to make use of the valve sizing software
"Refrigeration VASP", available from your local Siemens office.
The refrigeration capacity Q
0
is calculated by multiplying the mass flow by the specific
enthalpy differential found in the h, log p-chart for the relevant refrigerant. To help de-
termine the refrigeration capacity more easily, a selection chart is provided for each
application (from page 15). With direct or indirect hot-gas bypass applications, the en-
thalpy differential of Q
c
(the condenser capacity) must also be taken into account when
calculating the refrigeration capacity.
If the evaporating and/or condensing temperatures are between the values shown in
the tables, the refrigeration capacity can be determined with reasonable accuracy by
linear interpolation (refer to the application examples from page 14).
At the operating conditions given in the tables, the permissible differential pressure
∆p
max
(25 bar) across the valve is within the admissible range for these valves.
If the evaporating temperature is raised by 1 K, the refrigeration capacity increases by
about 3 %. If, by contrast, subcooling is increased by 1 K, the refrigeration capacity
increases by about 1 to 2 % (this applies only to subcooling down to approximately
8 K).
Connection type
1)
4-wire connection
3-wire connection
Notes