User Guide
Table Of Contents
Intended Operation Environment
Tunneled Network Deployment
4
A6V11979523_en_b
21 | 26
4.3 Tunneled Network Deployment
VPN (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virtual_private_network) is a solution for
making a virtual network. A technique called tunneling is used in the VPN and
enables users to create a virtual network between two remote points on an existing
public IP network and communicate freely.
With tunneling technology, packets transmitted on a physical communication
medium (such as, conventional network cable or optical fiber) are encapsulated as
data of another protocol (such as, TCP/IP packets) without directly transmitting on
a physical network. Encryption and electronic signature can be added
simultaneously when encapsulating. Encapsulated data is transmitted through a
session called a tunnel between the start and end point of the VPN communication.
The other party who receives the encapsulated data removes the original packets
from the capsules. If data is encrypted when encapsulated, it must be decrypted. If
an electronic signature has been added, the user can check whether the contents
of the packet have been tampered during transmission by testing the integrity of
the electronic signature.
When VPN communication must be carried out, because the data transmitted
between the computer sending the data and the computer receiving the data
travels through the tunnel is sent encapsulated, unprotected data is never exposed
on the network.
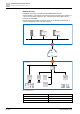
Fig. 8: Structure and operating principle of common VPN
Zone Border Protection and NK823x devices are Single Points of Failure for every
remote connection. Therefore, for each installation, it must be determined whether
it is acceptable that multiple remote connections can be made to one protection
component or the remote connections must be placed on separate zone
boundaries protection components and distributed to separate NK823x devices.
The second case is safer because breaching one of the protected zones can
compromise only one subnetwork while the others remain safe. Conversely, in the
first case, by breaching the only protected zone, the whole network is
compromised.
Client PC VPN Tunnel
Public IP Network
(for example,
the Internet)
Office LAN
Packets