User Manual
Valve sizing with correction factor
The applications and tables on the following pages are designed for help with selecting
the valves. To select the correct valve, the following data is required:
•
Application
−
Expansion (starting on page 9)
−
Hot-gas (starting on page 12)
−
Suction throttle (starting on page 14)
•
Refrigerant type
•
Evaporating temperature t
o
[°C]
•
Condensing temperature t
c
[°C]
•
Refrigeration capacity Q
o
[kW]
To calculate the nominal capacity, use the following formula:
•
k
vs
[m³/h] = Q
0
[kW] / K...*
*
K...
for expansion = KE
for hot-gas =
KH
for suction throttle =
KS
•
The theoretical k
v
value for the nominal refrigeration capacity of the plant should not
be less than 50 % of the k
vs
value of the selected valve
•
For accurate valve sizing, the valve selection program «Refrigeration VASP» is
recommended
The application examples on the following pages deal with the principles only. They do
not include installation-specific details such as safety elements, refrigerant collectors,
etc.
Use of the MVF661…N as an expansion valve
•
Typical control range 20...100 %.
•
Increased capacity through better use of the evaporator
•
The use of 2 or more compressors or compressor stages significantly increases
efficiency with low loads
•
Especially suitable for fluctuating condensing and evaporating pressures
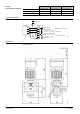
40153A
1
2
4
3
1 = MVL661…N
2 = evaporator
3 = compressor
4 = condenser
Capacity optimization
Electronic superheat control is achieved by using additional control equipment
(e.g. PolyCool).
Application example
Refrigerant R407C; Q
o
= 205 kW; t
o
= –5 °C; t
c
= 35 °C
The correct k
vs
value for the MVL661…N valve needs to be determined.
The important section of table KE for R407C (see page 12) is the area around the
working point. The correction factor KE relevant to the working point should be
determined by linear interpolation from the 4 guide values.
In practice, the KE, KH or KS value can be estimated because the theoretical k
vs
-value
ascertained will be rounded off by up to 30 % to 1 of the 10 available k
vs
-values. So you
can proceed directly with Step 4.
Note on interpolation
9/16
Building Technologies Refrigerant Valves PN 40 CE2N4716en
HVAC Products 08.06.2005