Data Sheet for Product
Technical Instructions Powertop Two-Way Valves Normally Open
Document No. 155-310P25
July 18, 2012
Page 4 Siemens Industry, Inc.
Table 6. Body Temperature-Pressure Rating.
Pressure
psig (Kvs)
Temperature
°F (°C)
ANSI Class 250
-20 to 150 (-30 to 66) 400 (2758)
200 (93) 385 (2655)
250 (121) 365 (2586)
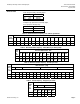
18
10 20 30 40 50
PRESSURE DIFFERENTIAL - psi
2-6 psi
10-14 psi
SPRING
RANGE
DIAPHRAGM AIR PRESSURE - psi
FOR CLOSE - OFF
60 70 80 90 100
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
VP0121R2
.5", .75", 1", 1.25" 10 to 14 psi
.5", .75", 1", 1.25" 2 to 6 psi
Figure 1. Nominal Close-off Ratings.
Operation
The actuator spring provides the necessary force to hold the stem in the raised or
normal position.
An increase in control pressure overcomes the spring pressure and moves the stem
downward. An increase in pressure decreases the flow of fluid though the valve.
With the loss of control pressure, the spring returns the valve to its normal position.
Sizing
The sizing of a valve is important for correct system operation. An undersized valve will
not have sufficient capacity at maximum load. An oversized valve can initiate cycling,
and the seat and throttling plug can be damaged because of the restricted opening.
Correct sizing of the control valve for actual expected conditions is essential for good
control.
Some variables that must be determined are:
• The medium to be controlled: water, etc.
• The maximum inlet temperature and pressure of the medium at the valve.
• The pressure differential that will exist across the valve under maximum load
demand.
• The maximum capacity the valve must deliver.
• The maximum line pressure differential the valve actuator must close against.
See
Table 2 through Table 5 for valve capacities.